Figure 3.
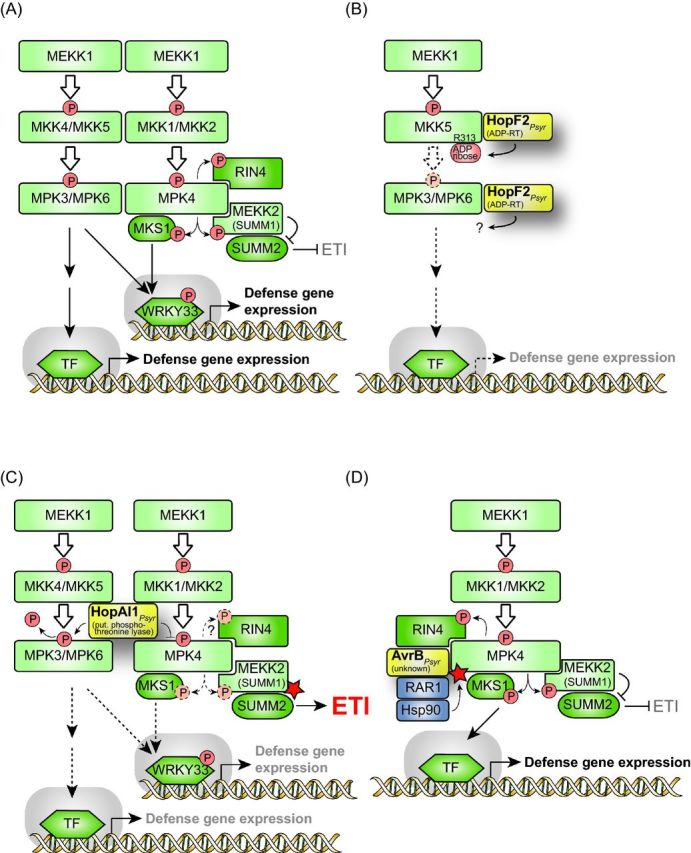
Influence of type III effectors on MAPK signaling pathways. (A) Schematic overview on MAPK signaling pathways involved in plant defense responses. During plant defense responses, two MAPK signaling pathways are activated which involve (i) MPK3/MPK6 and MKK4/MKK5 and (ii) MPK4 and MKK1/MKK2, respectively. The MP2Ks of both pathways are activated by the MP3K MEKK1, however, MPK3 and MPK6 can also be activated independently of MEKK1 (Suarez-Rodriguez et al.2007). The activation of MAPKs directly or indirectly leads to the release of transcription factors (TFs), which trigger the expression of defense genes. Known substrates of MPK4 are MKS1, RIN4 and the MP3K MEKK2 (also designated SUMM1). Phosphorylation of MKS1 by MPK4 leads to the release of the MKS1-bound TF WRKY33, which subsequently activates gene expression. MPK4 also phosphorylates the MAP3K MEKK2 and presumably results in its inactivation. MPK4-mediated inactivation of MEKK2 leads to the suppression of ETI responses triggered by the CC-NB-LRR R protein SUMM2, which likely guards MEKK2 (see the text for details). (B) HopF2 from P. syringae interferes with MPK3/MPK6 signaling pathway. The mono-ADP-RT HopF2 ADP-ribosylates and thus inactivates MKK5 and suppresses the MPK3/MPK6-mediated signaling pathway (indicated by dashed arrows). HopF2 also interacts with MPK6, yet, the outcome of this interaction is unknown. (C) The putative phosphothreonine lyase HopAI1 from P. syringae inhibits the activity of MAPKs. HopAI1 dephosphorylates MPK3 and MPK6 and thus interferes with the MPK3/MPK6 signaling pathway. Furthermore, HopAI1 suppresses the kinase activity of MPK4 and thus the phosphorylation of the MPK4 substrates MKS1 and MEKK2. It has not yet been shown whether HopAI1 also interferes with the MPK4-mediated phosphorylation of RIN4 (indicated by a dashed arrow and a questionmark). The loss of MPK4 activity leads to the activation of MEKK2 (indicated by a red asterisk), which in turn triggers SUMM2-mediated ETI (see the text for details). (D) AvrB from P. syringae activates MPK4. AvrB interacts with MPK4 and leads to its phosphorylation and thus activation. The efficient interaction between AvrB and MPK4 depends on RAR1, which presumably acts as a linker between AvrB and Hsp90. Hsp90 promotes the activity of MPK4 as is indicated by a red asterisk (see the text for details).
