Figure 4.
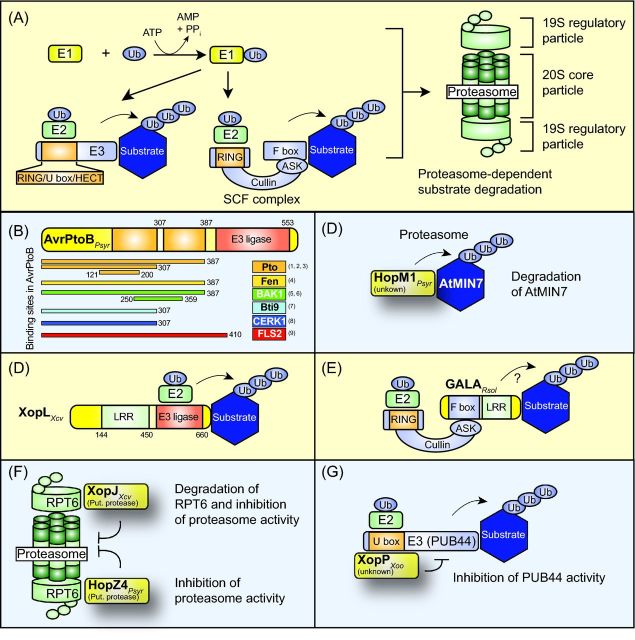
Contribution of type III effectors to proteasome-dependent protein degradation. (A) Model of the proteasome-dependent protein degradation pathway. Ubiquitin (Ub) is activated by the ubiquitin-activating enzyme (E1) and transferred to the ubiquitin-conjugating enzyme (E2), which interacts with the ubiquitin ligase (E3). E3 ubiquitin ligases are divided into several classes according to the presence of a HECT, RING or U-box domain. RING domain-containing E3 ubiquitin ligases can be part of a multimeric protein complex such as the SCF complex, which consists of a RING-box protein, the molecular scaffold protein cullin, an Arabidopsis SKP1-like protein (ASK1) and an F-box protein, which binds the substrate of the E3 ligase. E3 enzymes mediate the transfer of ubiquitin molecules to the substrate, thus leading to the formation of poly-ubiquitin chains, which allow the targeting of proteins to the proteasome. The proteasome consists of two 19S regulatory and a 20S core particle and catalyzes the unfolding and degradation of polyubiquitinated proteins. (B) Domain structure of the effector protein AvrPtoB from P. syringae. The regions of AvrPtoB, which provide binding sites for the AvrPtoB interaction partners Pto, Bti9, Fen, FLS2 and BAK1, are indicated. References: (1) Dong et al. 2009; (2) Xiao et al. 2007; (3) Mathieu, Schwizer and Martin 2014; (4) Rosebrock et al. 2007; (5) Shan et al. 2008; (6) Cheng et al. 2011; (7) Zeng et al. 2012; (8) Gimenez-Ibanez et al. 2009; (9) Göhre et al.2008. Experimental evidence for the presence of two Pto-binding sites in AvrPtoB (indicated as orange boxes) was reported by Mathieu, Schwizer and Martin (2014). Numbers refer to amino acid positions in AvrPtoB. (C) HopM1 from P. syringae induces the degradation of its interaction partner AtMIN7. The HopM1-mediated degradation of AtMIN7 depends on the activity of the proteasome. (D) The effector protein XopL from X. campestris pv. vesicatoria triggers the ubiquitination of plant proteins. XopL contains an N-terminal LRR and a C-terminal E3 ubiquitin ligase domain. The plant targets of XopL are unknown. Numbers refer to amino acid positions in XopL. (E) GALA proteins from R. solancearum contain an F-box domain and were proposed to associate with components of the SCF complex. In agreement with this hypothesis, an interaction between GALA proteins and ASK proteins has been shown. A contribution of GALA proteins to the ubiquitination of substrates of the SCF complex remains to be demonstrated. (F) XopJ from Xanthomonas spp. and HopZ4 from P. syringae interact with the proteasome subunit RPT6 and suppress the activity of the proteasome. XopJ leads to the degradation of RPT6. (G) XopP from X. oryzae pv. oryzae interacts with the U box E3 ubiquitin ligase PUB44 from rice and inhibits its activity.