Figure 6.
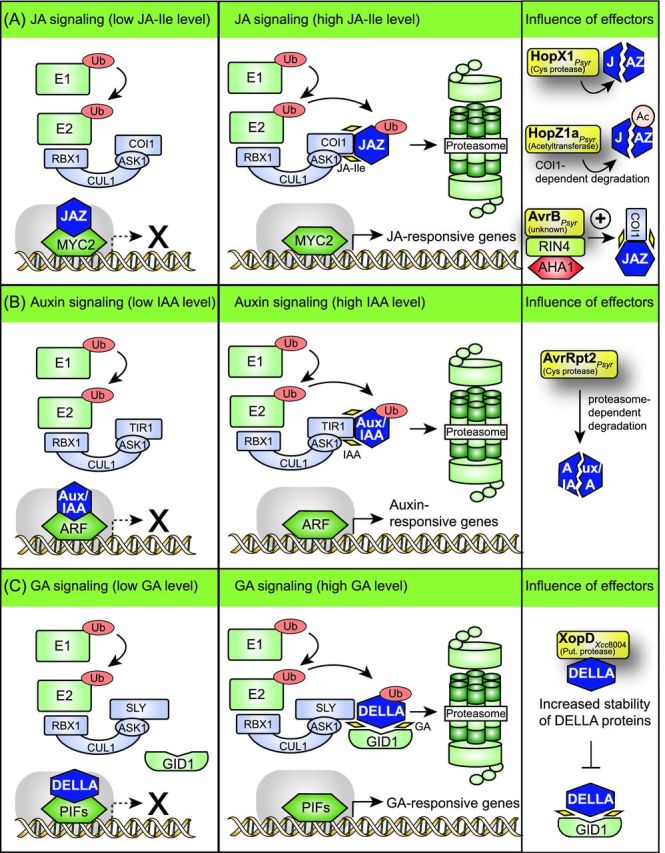
Modulation of JA, auxin and GA signaling pathways by type III effectors. (A) HopX1, HopZ1a and AvrB from P. syringae interfere with JA signaling pathways. Bioactive JA-Ile promotes the interaction between JAZ proteins and the F-box protein COI1, which is a component of the SCF complex. The subsequent degradation of JAZ proteins leads to the release of JAZ-interacting transcription factors (e.g. MYC2), which activate the expression of JA-responsive genes. The cysteine protease HopX1 directly or indirectly degrades several JAZ proteins independently of the JA receptor COI1 and thus activates the expression of JA-responsive genes. The acetyltransferase HopZ1a acetylates JAZ proteins and leads to their proteasome-dependent degradation. The effector protein AvrB from P. syrinage interacts with RIN4, which is a negative regulator of PTI and associates with the H+ ATPase AHA1. The interaction of AvrB with the RIN4-AHA1 complex promotes the interaction between JAZ proteins and COI1 and leads to the activation of JA-responsive genes. (B) Auxin signaling pathways are targeted by the cysteine protease AvrRpt2 from P. syringae. IAA promotes the interaction between Aux/IAA proteins and the F-box protein TIR1. This leads to the proteasome-dependent degradation of Aux/IAA proteins and to the release and activation of ARFs. ARFs subsequently activate the expression of auxin-responsive genes. The cysteine protease AvrRpt2 directly or indirectly induces the degradation of Aux/IAA proteins by the proteasome and thus activates the expression of auxin-responsive genes. (C) XopD from X. campestris pv. campestris strain 8004 interferes with the stability of DELLA proteins, which are negative regulators of GA-responsive genes. GA-dependent signaling is controlled by DELLA proteins, which inactivate PIF (phytochrome interacting factors) transcription factors. Binding of GA to its receptor GID1 leads to a conformational change in GID1, which subsequently binds to DELLA proteins. The formation of a GID1-DELLA complex promotes the interaction between DELLA proteins and the F-box protein SLY and thus the proteasome-dependent degradation of DELLA proteins. This leads to the release of PIF transcription factors, which activate the expression of GA-responsive genes. XopDXcc8004 presumably interferes with the binding of GID1 to DELLA proteins and delays the GA-induced degradation of the DELLA protein RGA. Notably, however, an influence of XopDXcc8004 on the transcription of GA-responsive genes has not yet been detected.
