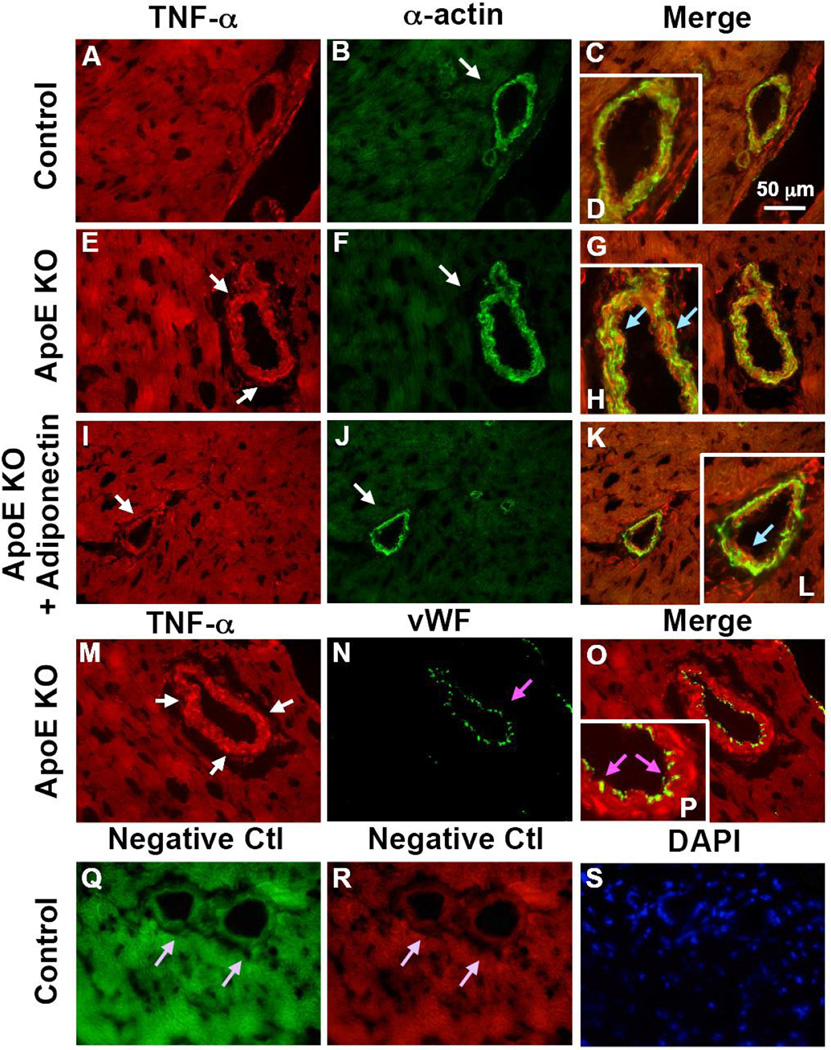
Figure 4. TNF-α is colocalized with vascular smooth muscle cells in coronary arterioles.
TNF-α is colocalized with vascular smooth muscle cells in coronary arterioles as shown by dual fluorescence labeling for TNF-α and markers for endothelial cells [von Willebrand factor (vWF)] and vascular smooth muscle cells (α-actin) on frozen heart sections. A, B, C and D, dual labeling of TNF-α (red) and α-actin (green) in control mice. E, F, G and H, dual labeling of TNF-α (red) and α-actin (green) in ApoE KO mice. I, J, K and L, dual labeling of TNF-α (red) and α-actin (green) in ApoE KO + Adiponectin mice. The arrows in E and I show staining of TNF-α (red) while the arrows in B, F and J show staining of vascular smooth muscle cells (green). The blue arrows in H and L indicate colocalization of TNF-α and vascular smooth muscle cells (yellow). M, N, O and P, dual labeling of TNF-α (red) and vWF (green) in ApoE KO mice. Enlargements of panels C, G, K and O are shown in panel D, H, L and P, respectively. The pink arrows in N and P show the specific vWF staining with absence of TNF-α staining. Q and R, negative control: the arrows show an absence of staining with primary antibodies being replaced by IgG-isotype controls. S shows nuclear staining with DAPI (blue) in control mice. Magnification ×40. Data shown are representative of 4 separate experiments.