Fig. 1. Programmable electromicrofluidic platform for microgel formation and architecture assembly.
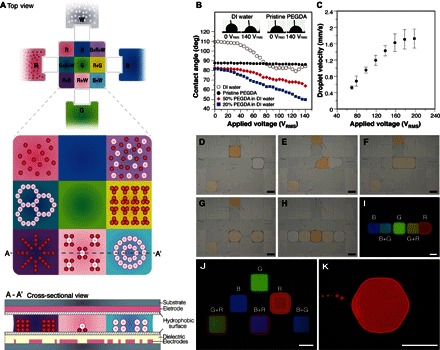
(A) Top and cross-sectional views of a conceptual electromicrofluidic platform that assembles an architecture consisting of 3 × 3 microgels prepared from four crosslinkable elementary materials (W, R, G, and B) through manipulations of suspended particles, liquid droplets, and crosslinked microgels by electrowetting and dielectrophoresis between parallel plates with appropriate electrodes and dielectric and hydrophobic layers. (B) Change of contact angle by electrowetting on sessile drops of water, PEGDA, and their mixtures with varied concentrations. DI, deionized; deg, degrees. (C) Moving velocity of a PEGDA droplet driven by dielectrophoresis on the electromicrofluidic platform. (D to H) Producing microgels by aliquoting, merging, mixing, splitting, and transporting, PEGDA droplets with rhodamine 6G (R6G) (R), fluorescein (G), and coumarin 450 (C-450) (B) dyes. (I) Crosslinking of single (G) and Janus binary (B/B+G and G+R/R) microgels after light exposure. (J) Microgels with configurable encoding colors by droplet manipulations (movie S1). (K) Hexagonal microgel. Scale bars, 1 mm.
