Fig. 4.
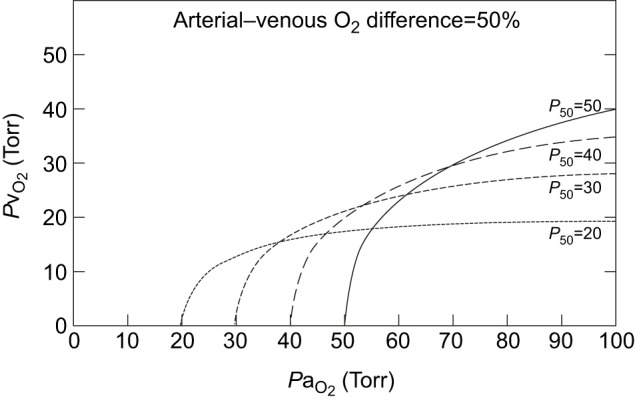
Isobars showing predicted values of venous PO2 (an index of tissue oxygenation) as a function of arterial PO2 at different values of blood P50, assuming 50% tissue O2 extraction and constant cardiac output. At normal or moderately reduced PaO2, a higher P50 results in a higher PvO2 (and hence improved tissue oxygenation). Under more severe hypoxemia, by contrast, a lower P50 results in a higher PvO2 while still maintaining constant O2 extraction.
