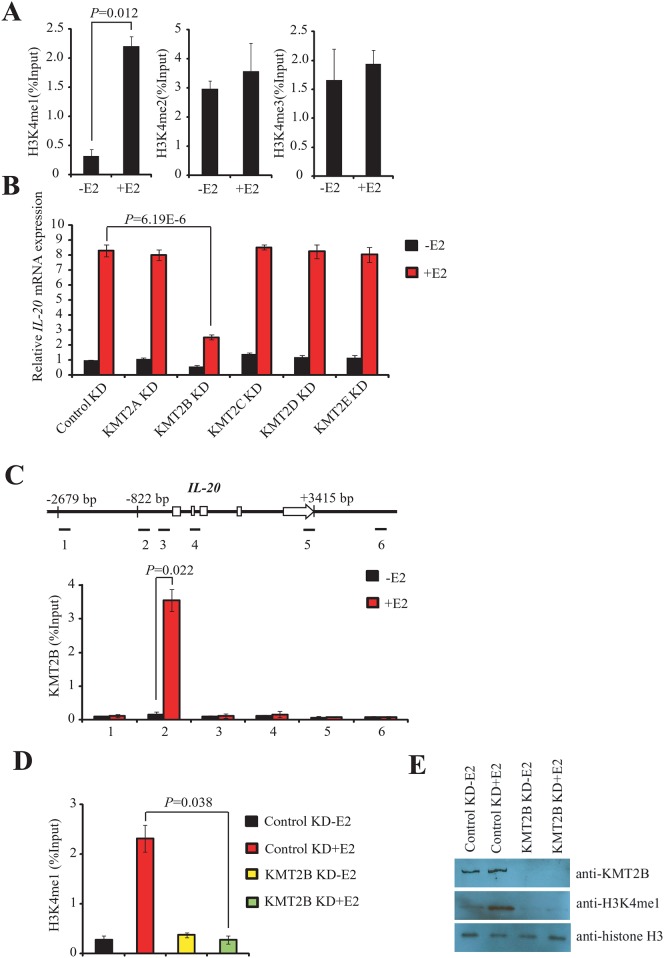
Fig 3. KMT2B regulates E2-mediated induction of IL-20 gene through the modification of H3K4.
(A) Enrichment analysis of the three H3K4 methylations (H3K4me1, H3K4me2, and H3K4me3) at the IL-20 promoter in MCF-7 cells using ChIP. The experiment was performed with or without E2. The mean and SD were calculated from at least three independent experiments. (B) Expression of IL-20 as determined by RT-qPCR in KMT2A, KMT2B, KMT2C, KMT2D, or KMT2E-depleted MCF-7 cells in the presence or absence of E2 and normalized against 18s rRNA. (C) Binding of KMT2B to the IL-20 promoter region as determined by ChIP assays. Upper panel: Schematic of the IL-20 locus (exons as open boxes) and the six amplicons (black segments). The specific anti-KMT2B antibody, ab104444, was used for the ChIP experiments. DNA isolated from immunoprecipitated chromatin was amplified by qPCR using designed primers. Lower panel: Bar chart showing the relative levels of KMT2B at each of the six IL-20 gene regions. The mean and SD were calculated from at least two independent experiments. (D) ChIP assays showing the depletion of H3K4me1 at the IL-20 promoter in KMT2B knockdown cells in the presence or absence of E2. The mean and SD were calculated from at least three independent experiments. (E) Western blotting of nuclear extracts prepared from MCF-7 cells transfected with control siRNA or KMT2B-siRNA in the presence or absence of E2. The antibodies used are shown in the right panel.