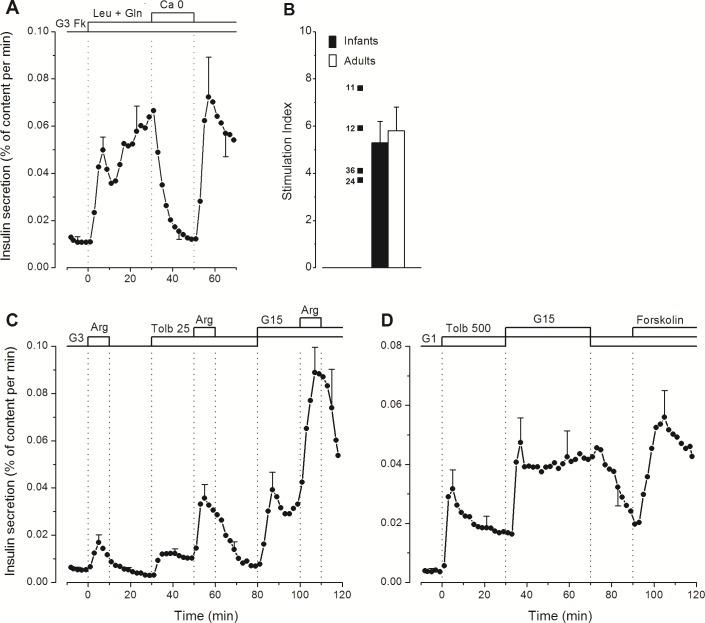
Fig 3. Effects of amino acids and tolbutamide on insulin secretion in perifused islets from human infants.
(A) The experiments were done in the presence of 3 mmol/l glucose (G3) and 1 μmol/l forskolin (Fk) throughout. Leucine and glutamine (5 mmol/l each) were added at 0 min. Between 30 and 50 min, CaCl2 was omitted and 100 μmol/l EGTA was added. (B) Insulin secretion induced by leucine + glutamine was expressed as a stimulation index for the whole response (0–30 min). Mean and individual values for islets from four infants (identified by age in months) are compared with mean values for 5 islet preparations from normal adults [33]. (C) Three pulses of 10 mmol/l arginine (Arg) were applied in G3 alone, G3 + 25 μmol/l tolbutamide (Tolb 25), or G15 + Tolb 25. (D) Islets were fully depolarized by 500 μmol/l tolbutamide (Tolb 500) in 1 mmol/l glucose (G1). The glucose concentration was then increased to 15 mmol/l (G15) between 30 and 70 min, and forskolin (1 μmol/l) was eventually added to G1 (in 3/5 cases only). Values are means ± SE for islet preparations from 4 (A, B and C) or 5 infants (D).