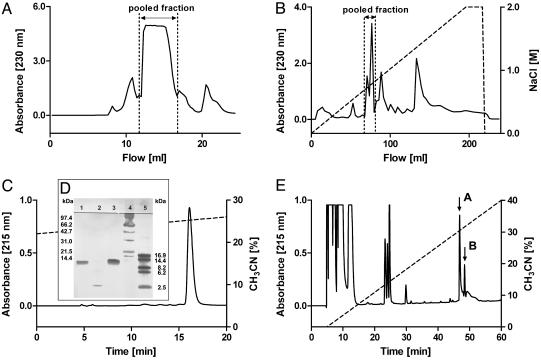
Fig. 1.
Isolation of CSTX-13 from the venom of C. salei.(A) Crude venom was first separated by gel filtration on a Superdex 75 column. (B) Further separation of the pooled fraction was achieved by cationic exchange chromatography on a Mono S HR column. (C) When RP-HPLC was used, CSTX-13 was finally isolated on a nucleosil 100–5C8 column, and the purity was controlled by SDS/PAGE. (D) Lanes: 1, native CSTX-13; 2, reduced CSTX-13; 3, native CSTX-1; 4, molecular mass markers (14.4–97.4 kDa; Bio-Rad); and 5, molecular mass markers (2.5–16.9 kDa; Amersham Pharmacia). (E) RP-HPLC of reduced and alkylated CSTX-13 on a nucleosil 100–5C8 column resulted in the separation of chain A (first arrow) and chain B (second arrow).