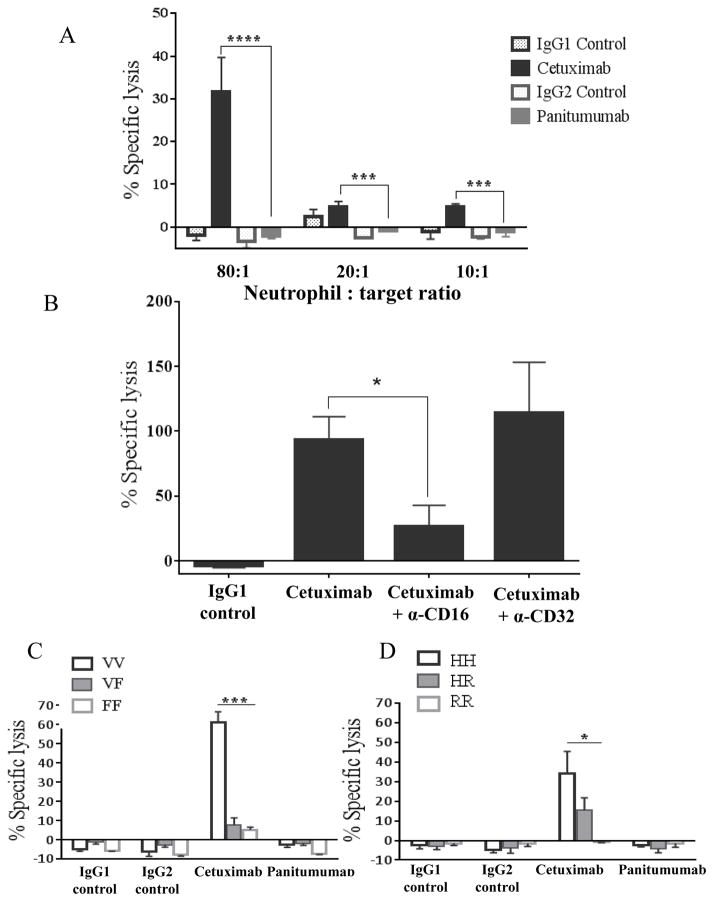
Figure 3. Cetuximab-activated neutrophil mediated ADCC is enhanced in donors who are homozygous for FcγIIIa VV genotype and FcγIIa HH genotype.
(A) Negatively isolated neutrophil co-cultured for 4h with 51Cr labeled JHU-029 HNSCC cells coated with 10 μg/mL of cetuximab, panitumumab or isotype controls (IgG1 or IgG2) at different E:T ratios (10:1, 20:1 and 80:1). Cetuximab-activated neutrophils mediate ADCC above isotype controls whereas panitumumab-activated neutrophils do not. (B) JHU-029 HNSCC cells pre-treated with either CD16 or CD32 blocking antibodies for 30 minutes, washed once, then labeled with 51Cr, then co-cultured with negatively isolated neutrophils for 4h in the presence of cetuximab or IgG1 control antibody (10 μg/mL) at an 80:1 E:T ratio. Cells pre-treated with CD16 blocking antibody show a reduction in cetuximab-activated neutrophil mediated ADCC compared with non-pretreated cells and cells pre-treated with CD32 blocking antibody. (C) Neutrophils from donors separated by FcγRIIIa and FcγRIIa genotype co-cultured for 4h with 51Cr labeled JHU-029 HNSCC cells coated with 10 μg/mL of cetuximab, panitumumab or isotype controls (IgG1 or IgG2) at 80:1 E:T ratio. Neutrophils from FcγRIIIa VV donors demonstrate significantly enhanced ADCC activity compared with VF and FF donors. (D) Neutrophils from FcγRIIa HH donors mediate enhanced ADCC compared with HR and RR donors. Data are mean + SEM,*p<0.05, ***p< 0.001, ****p< 0.0001.