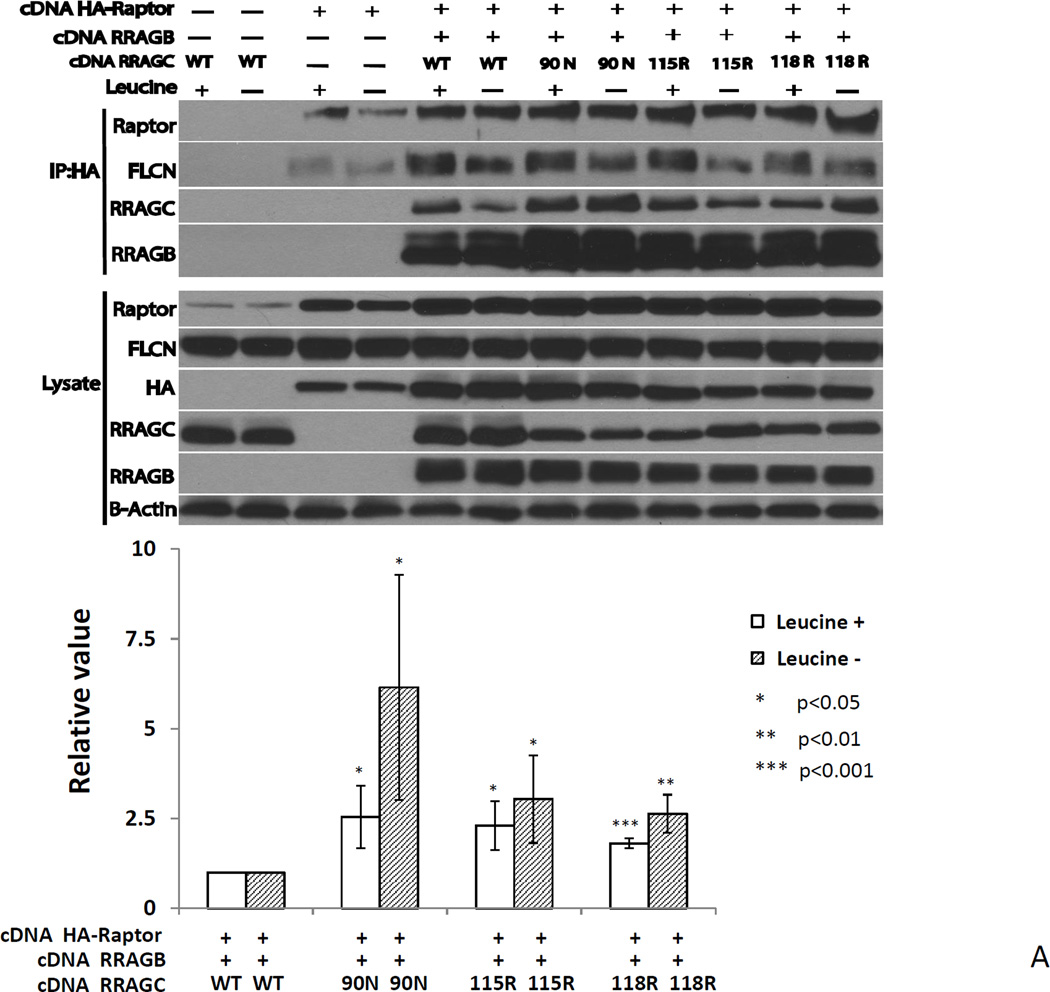
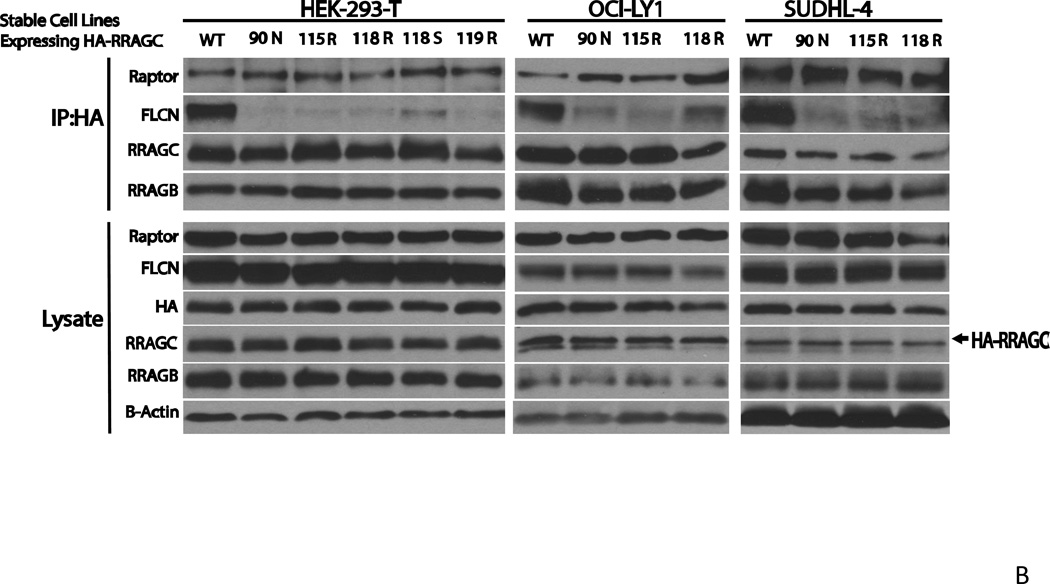
Figure 5.
A RRAGC mutants demonstrate increased HA-RPTOR binding in co-immunoprecipitation studies in transiently transfected HEK293T cells. Upper: HEK293T cell were transiently co-transfected as indicated with expression plasmids coding for HA-RPTOR, RRAGB, RRAGC WT or the indicated RRAGC mutants. CHAPS detergent lysates were prepared and subjected to anti-HA-bead conjugate-mediated immunoprecipitations. Bound protein was eluted and fractioned by SDS-PAGE and prepared for immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. Leucine starvation (Leu −) was performed in parallel transfections. Lysate: aliquots of lysates prior to immunoprecipitation. Lower: Displayed are combined quantitation results (RRAGC IP band intensities divided by RRAGC detergent cell lysates band intensities normalized to raptor IP band densities) from 3 independent experiments using ImageJ densitometry results indexed to the measurements for RRAGC wt.
B Decreased co-immunoprecipitation of FLCN with HA-RRAGC mutants in stably transduced HEK293T cells or lymphoma cell lines. Stable HA-RRAGC WT or mutant transduced HEK293T cells or the LY1 and SUDHL4 lymphoma cell lines were used. CHAPS detergent lysates were prepared and subjected to anti-HA-bead conjugate-mediated immunoprecipitations. Bound protein was eluded and fractioned by SDS-PAGE and prepared for immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies. Lysate: aliquots of lysates prior to immunoprecipitation. The position of transduced HA-RRAGC is marked by an arrow.