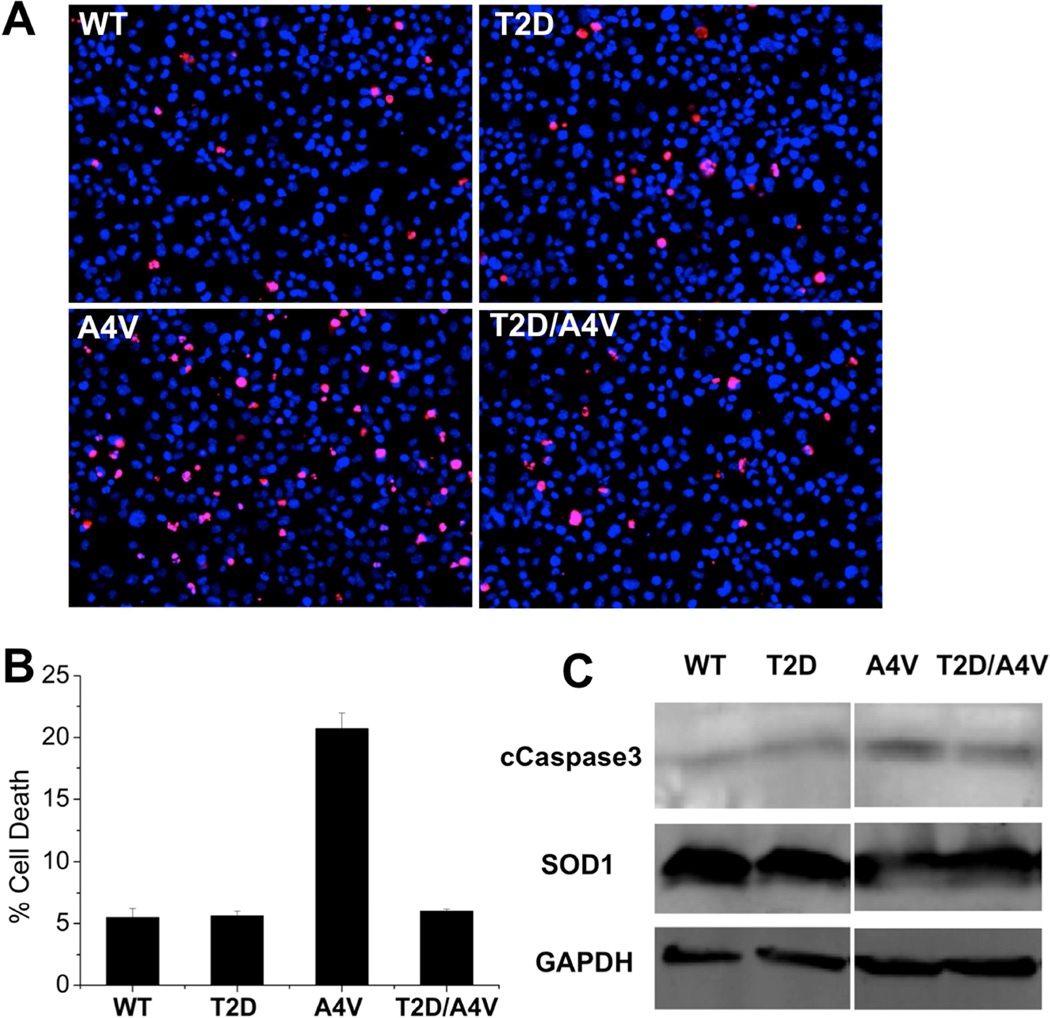
Figure 3. T2D mutation reduces the cytotoxic effect of A4V in motor neuron-like cells.
(A) Transfection of NSC-34 cells with T2D-SOD1 and WT-SOD1 (negative control) led to similar cell death ratio. A4V–SOD1 transfection (positive control) decreased cell viability and T2D/A4V–SOD1 rescued cells from A4V–SOD1 mediated cytotoxicity. Applied three days post-transfection, red stain (propidium iodide) identifies dead cells, while blue stain (Hoechst) identifies all cell population. (B) Average cell death rates are measured as the percentage of red stained cells: WT 5.4%, T2D 5.6%, A4V 20.7% and T2D/A4V 6.0%. Each bar represents the standard error of the mean, n=3. (C) Levels of the apoptotic marker cCaspase 3 in NSC-34 cells demonstrated by western blot confirm the protection role of T2D mutation, as T2D/A4V leads to reduced expression of cCaspase 3. The normalized expression levels: WT 100%, T2D 89%, A4V 377% and T2D/A4V 135%.