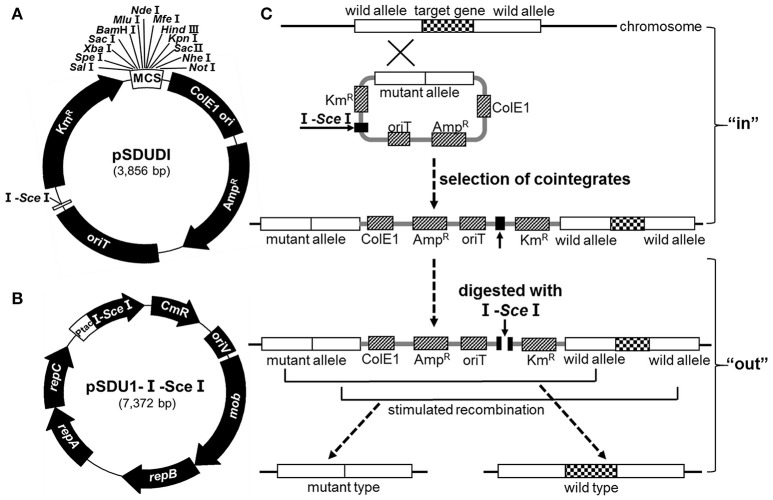
Figure 2.
The markerless gene knockout strategy in A. caldus. (A) Map of the suicide plasmid pSDUDI. ColE1, the replication origin; oriT, the origin of transfer; I-SceI, endonuclease recognition site. (B) Plasmid pSDU1-I-Sce I. I-Sce I endonuclease gene was under the control of Ptac promoter. (C) General scheme of the markerless gene knockout method. At the “in” step, the suicide plasmid carrying homologous sequences specific to the targeted gene was conjugated into A. caldus, and integrated into the chromosome with the help of Rec homologous recombination system in A. caldus. At the “out” step, the I-Sce I endonuclease encoded by plasmid pSDU1-I-Sce I created the double-stranded breaks (DSBs) on the chromosome, which acted as the signal to stimulate a second recombination event, generating either a wild type or a mutant type.