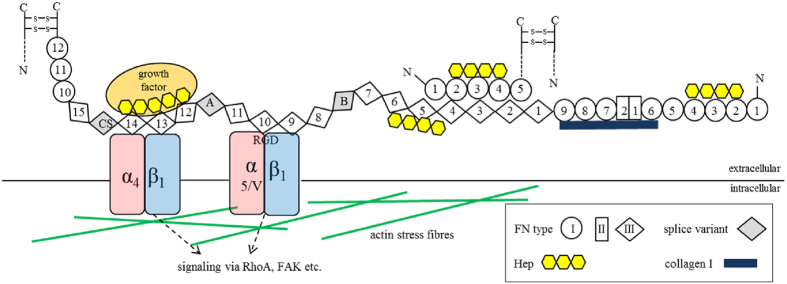
Figure 1. Domain structure and binding partners of FN.
FN is secreted as a disulfide-bonded homodimer, which is composed of three types of repeating modules (FNI, FNII and FNIII) numbered serially. Splice variants may additionally contain extra domains A (EDA) or B (EDB) and a variable region CS (connecting segment) (all in grey). FN has several binding domains for interaction partners in the ECM like collagen I (dark blue) or growth factors (orange). Each FN chain has three Hep binding regions (yellow) located at FNI2-4, FNIII4-6 and FNIII12-14, respectively. The antiparallel, intermolecular interaction of FNI1-5 and FNIII1-5 is crucial for FN fibrillogenesis. The RGD binding site is located at FNIII10 and is recognized by integrins α5β1, αVβ1 and αVβ3 (red and blue). Several intracellular processes are directly affected by integrins through cytoskeletal adapter (actin in green) and signaling molecules as FAK (focal adhesion kinase) and small GTPases as RhoA.