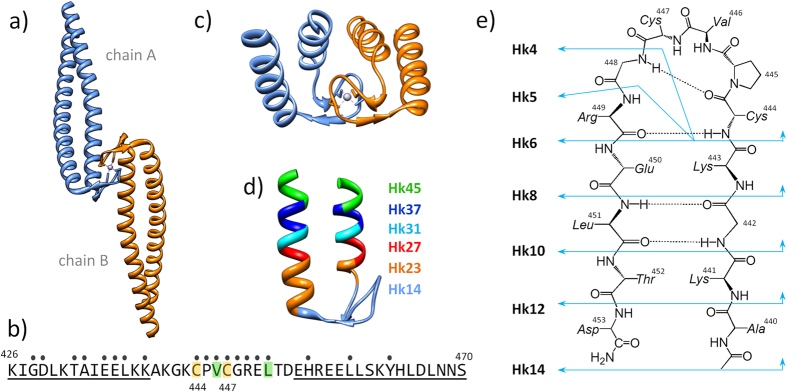
Figure 1. Structure of the central fragment of the Rad50 protein from P. furiosus.
(a) Crystal structure of the 103-amino acid-long central fragment of Rad50, representing the zinc hook domain (PDB code: 1L8D)6; (b) Sequence of the 45-amino acid Hk45 protein fragment used as a domain model in the present study. The dots indicate all residues forming the dimer interface, obtained using the PDBePISA web server. Val446 and Leu451 (green) residues were examined for the formation of hydrophobic interactions19. Cys444 and Cys447, which participate in Zn2+ binding, are shown in yellow. The underlined residues participate in coiled-coil formation; (c) Structural representation of the 45-amino acid-long fragment of the domain; (d) Zinc hook peptides (Hk23-Hk45) used in the present study to probe the effect of coiled-coil formation; and (e) Zinc hook peptides (Hk4-Hk14) used in the present study to probe the effect of β-hairpin formation.