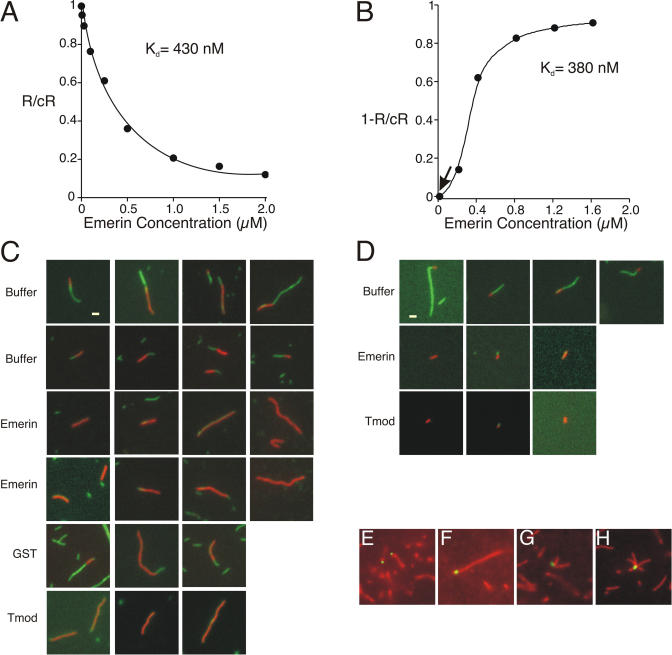
Figure 3. Emerin Binds the Pointed End of Actin Filaments.
(A) Gelsolin–actin seeds were incubated with increasing concentrations of wild-type emerin residues 1–222. Emerin significantly reduced the rate of subunit addition at the pointed end, with an apparent Kd of 430 nM (range, 300–500 nM, n = 12). R, rate of polymerization in the presence of emerin; cR, control rate of polymerization (actin alone).
(B) Emerin inhibits depolymerization of actin filaments (2 μM) preformed from gelsolin–actin seeds, with an apparent Kd of 380 nM (range, 350–450 nM, n = 6). R, rate of depolymerization in the presence of emerin; cR, control rate of depolymerization (actin alone).
(C) Rhodamine–phalloidin-stabilized actin filaments were formed from 2 μM actin, then capped at the barbed end by the addition of 100 nM capping protein, and finally diluted 2-fold in the presence of buffer or 1 μM emerin, GST, or tropomodulin (Tmod). Samples were then incubated with actin (3.2 μM) and Alexa-488 phalloidin (3.2 μM) for 2 min, diluted 1:500, placed on polylysine-coated coverslips, and viewed by fluorescence microscopy. Bar is 1 μm and applies to all panels.
(D) Actin (2 μM) was incubated with gelsolin–actin seeds (500 nM) in the presence of rhodamine–phalloidin (2 μM). These red filaments were diluted 10-fold and incubated with buffer alone or with 1 μM emerin or tropomodulin (Tmod) for 10 min, followed by incubation with actin (2 μM) and Alexa-488-labeled (green) phalloidin (2 μM) for 2 min. Samples were diluted 1:500, placed on polylysine-coated coverslips, and viewed by fluorescence microscopy. Bar is 1 μm and applies to all panels.
(E–H) Alexa-488-labeled emerin (green) was incubated 30 min with actin filaments stabilized by Alexa-546 phalloidin (red) and centrifuged at 100,000g to recover filaments, which were diluted 1:500 for viewing.