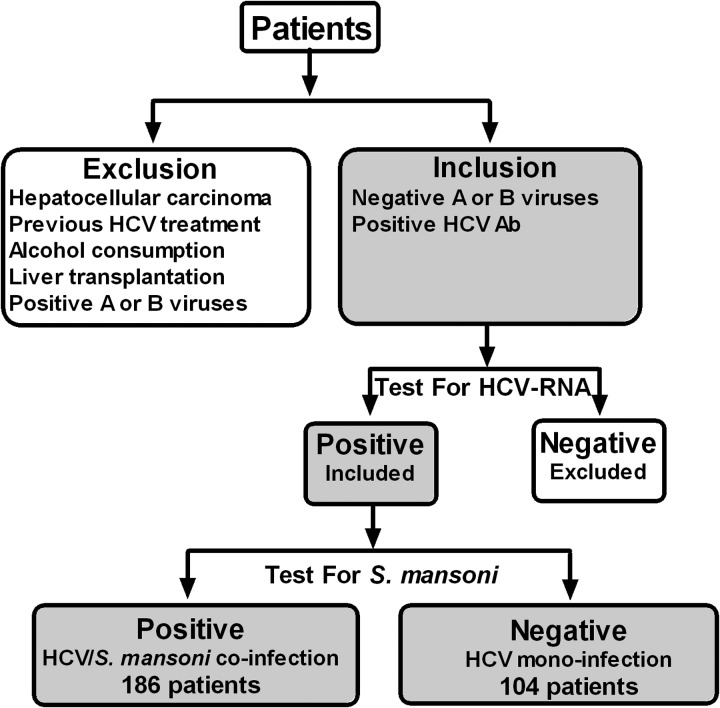
Figure 1.
A flowchart showing the selection process of patients included in this study. Hepatitis C virus (HCV) diagnosis was based on a positive test for anti-HCV antibodies. Patients were then confirmed for the presence of HCV-RNA using polymerase chain reaction assay. HCV-monoinfected patients had no history or laboratory evidence of previous or current Schistosoma mansoni infection. The diagnosis of S. mansoni was based on detecting vital or dead schistosomal ova in stools or rectal biopsy with seropositivity to schistosomal antibodies. Patients with serological evidence of active hepatitis A or B viruses, history of habitual alcohol consumption, hepatocellular carcinoma, previous interferon treatment, and liver transplantation were excluded from the present study.