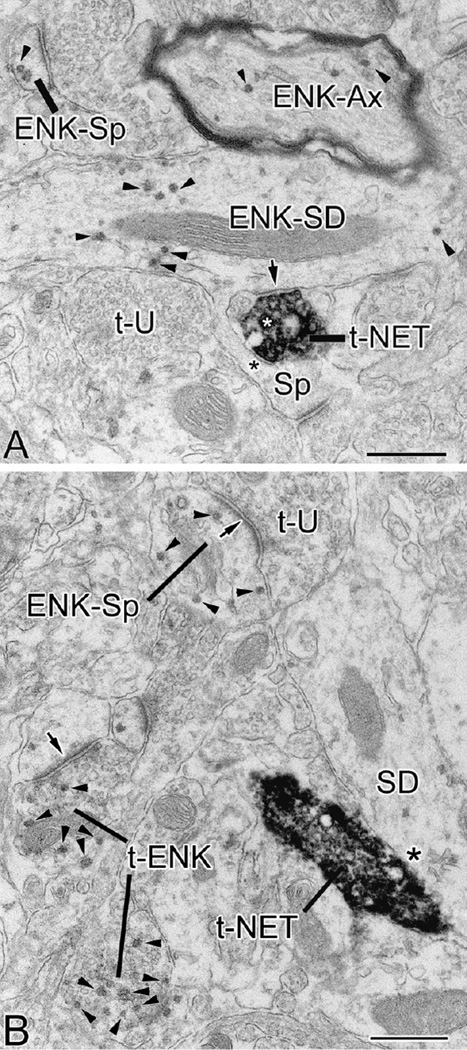
Fig. 1.
Photomicrographs of ENK-ir in the BLC in sections stained with nickel-intensified DAB. (A) ENK-ir at the bregma −2.2 level. Note strong ENK-ir in the central nucleus (including its lateral capsular subdivision [CLC]) and caudate-putamen (CP), and moderate ENK-ir in the intercalated nuclei located in the external capsule along the lateral (left) border of the anterior subdivision of the basolateral nucleus (BLa). The BLa and dorsolateral subdivision of the lateral nucleus (Ldl) have light neuropilar ENK-ir and scattered nonpyramidal neurons that exhibit intense ENK-ir (see C for a view of the BLa at higher magnification). (B) ENK-ir at the bregma −3.0 level. Note strong ENK-ir in the central nucleus (including its lateral subdivision [CL]), caudate-putamen (CP), and intercalated nuclei (including one located at the border of the lateral and basolateral nuclei [IN]). All nuclei of the BLC, including the dorsolateral, ventromedial and ventrolateral subdivisions of the lateral nucleus (Ldl, Lvm, Lvl), the anterior, posterior and ventral subdivisions of the basolateral nucleus (BLa, BLp, BLv), and the anterior basomedial nucleus (BMa) have light neuropilar ENK-ir and scattered nonpyramidal neurons that exhibit intense ENK-ir (see D and Fig. 2A for higher power views of the BLa at this level). The stronger neuropilar staining of the lateral nucleus versus the other nuclei of the BLC is due to a higher density of ENK+ axons in this nucleus (see Fig. 2B). (C and D) Higher power photomicrographs of the ventral parts of BLa shown in A and B, respectively (asterisks mark the same blood vessels in A/C and B/D). Note intense ENK-ir in small nonpyramidal neurons (arrows show three representative examples in each pane). In addition, there are numerous larger putative pyramidal neurons with light ENK-ir in the ventral part of BLa (C; above the blood vessel marked with an asterisk) and ventromedial corner of BLa (D; below and to the right of the blood vessel marked with an asterisk) (arrowheads show four representative examples in each pane). Scale bars = 200 µm in A (B is at the same magnification), 100 µm in C (D is at the same magnification).