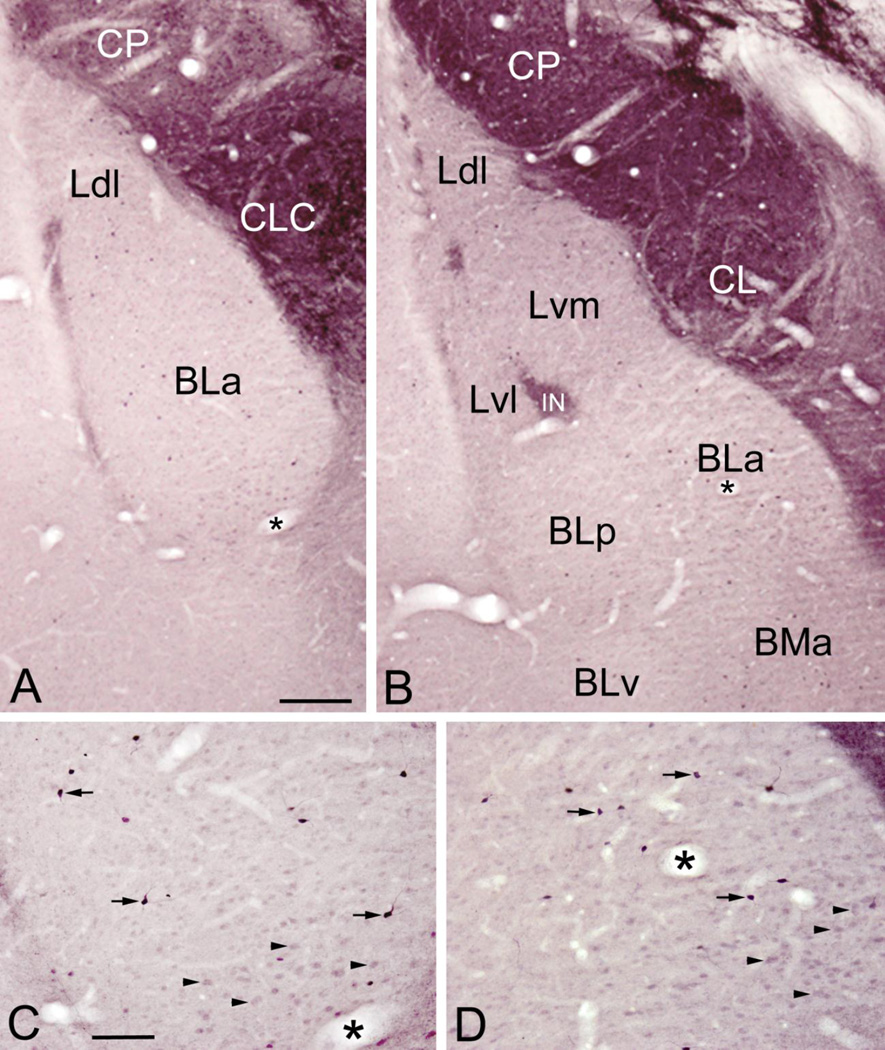
Fig. 3.
Plots of ENK+ nonpyramidal neurons in the BLC and cortical nuclei at rostral (A), middle (B) and caudal (C) levels of the amygdala. Drawings of brain sections are from the atlas by Paxinos and Watson (1997). Neurons are plotted from two non-adjacent sections at each level. Each dot represents one neuron. The central nucleus and intercalated nuclei contained a much higher density of neurons, but these are not plotted. Abbreviations: ACo, anterior cortical nucleus; AHA, amygdalohippocampal area; AStr, amygdalostriatal transition area; BLa, anterior basolateral nucleus; BLp, posterior basolateral nucleus; BLv, ventral basolateral nucleus; BMa, anterior basomedial nucleus; BMp, posterior basomedial nucleus; CL, lateral central nucleus; CeC, capsular central nucleus; CM, medial central nucleus; CP, caudate-putamen; IN, intercalated nucleus; Ldl, dorsolateral lateral nucleus; Lvm, ventromedial lateral nucleus; Lvl, ventrolateral lateral nucleus; Mad, anterodorsal medial nucleus; Mav, anteroventral medial nucleus; Mpd, posterodorsal medial nucleus; Mpv, posteroventral medial nucleus; OT, optic tract; PC, piriform cortex; PLCo, posterolateral cortical nucleus; PMCo, posteromedial cortical nucleus; ST, stria terminalis; VEn, ventral endopiriform nucleus.