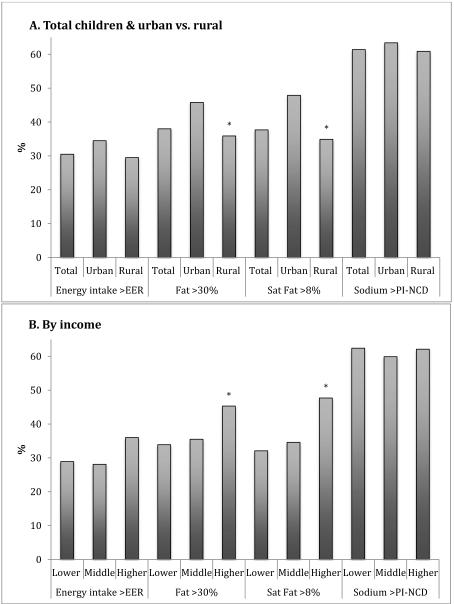
Figure 2. Prevalence (%) of excessive intakes of energy, total fat, saturated fat and sodium by area of residence and income among children 7-12 y who participated in the China Health and Nutrition Survey 2009.
Estimates presented as %. Excessive intakes were calculated using EER for energy, AMDR for total fat and saturated fat, and Chinese Proposed Intakes (PI-NCD) for sodium; 2014 Dietary Reference Intakes for the Chinese Population.
* Significantly different between urban vs. rural; or between lower vs. middle or higher income, Student’s t test, p<0.05.