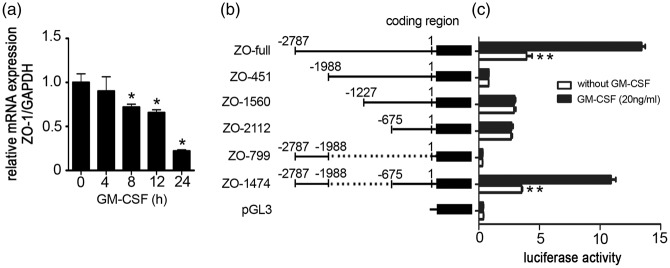
Figure 4.
Effect of GM-CSF on ZO-1 promoter activity and the GM-CSF-responsive region of the ZO-1 promoter. (a) GM-CSF affects ZO-1 transcription. GM-CSF was incubated with an HBMEC monolayer for the indicated time points, and mRNA expression levels were estimated by real-time RT-PCR. Values are shown as means ± standard deviations from three separate experiments. One-way ANOVA was used for repeated measurements. *p < 0.05 vs. normal HBMECs. (b) Schematic representation of different ZO-1 promoter deletion constructs. Numbers indicate the number of base pairs from the transcription start site. (c) Luciferase activities of the corresponding constructs in HBMECs. HBMECs were transfected with different ZO-1 promoter deletion mutants, and the luciferase reporter activity levels were detected 48 h after transfection. Results were normalized relative to Renilla-driven luciferase activity and expressed as means ± standard errors of the data from three separate experiments. **p < 0.01 vs. ZO-1 promoter luciferase activity in HBMECs without GM-CSF stimulation.