Figure 4.
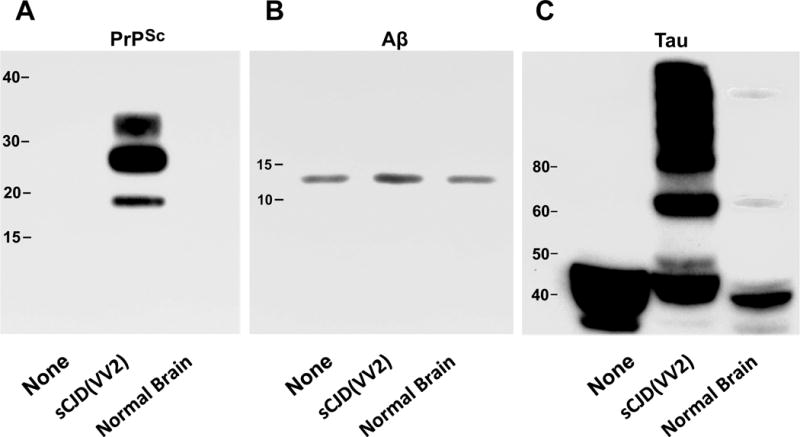
Western immunoblots stained for scrapie-associated prion protein (PrPSc), β-amyloid peptide (Aβ42), and tau protein in 20 pooled human brain aggregates (Hu BrnAggs). Each set of BrnAggs were either not treated (None), treated with a human brain homogenate from a patient with sporadic Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease (sCJD(VV2)), or treated with a normal human brain homogenate (Normal Brain). (A) All 3 of the treatments were exposed to Proteinase K to show protease resistant PrPSc. (B) Antibodies to Aβ peptide showed that sCJD(VV2) exposure resulted in an increased level of Aβ in the BrnAggs while None and Normal Brain exposure did not. (C) Antibodies to tau protein showed that sCJD(VV2) was the only treatment that caused a large amount of phosphorylated tau with molecular masses greater than 60 kDa to be generated. The Normal Brain homogenate generated very small bands at 60 kDa and greater than 100 kDa. Molecular weights are indicated in each immunoblot.
