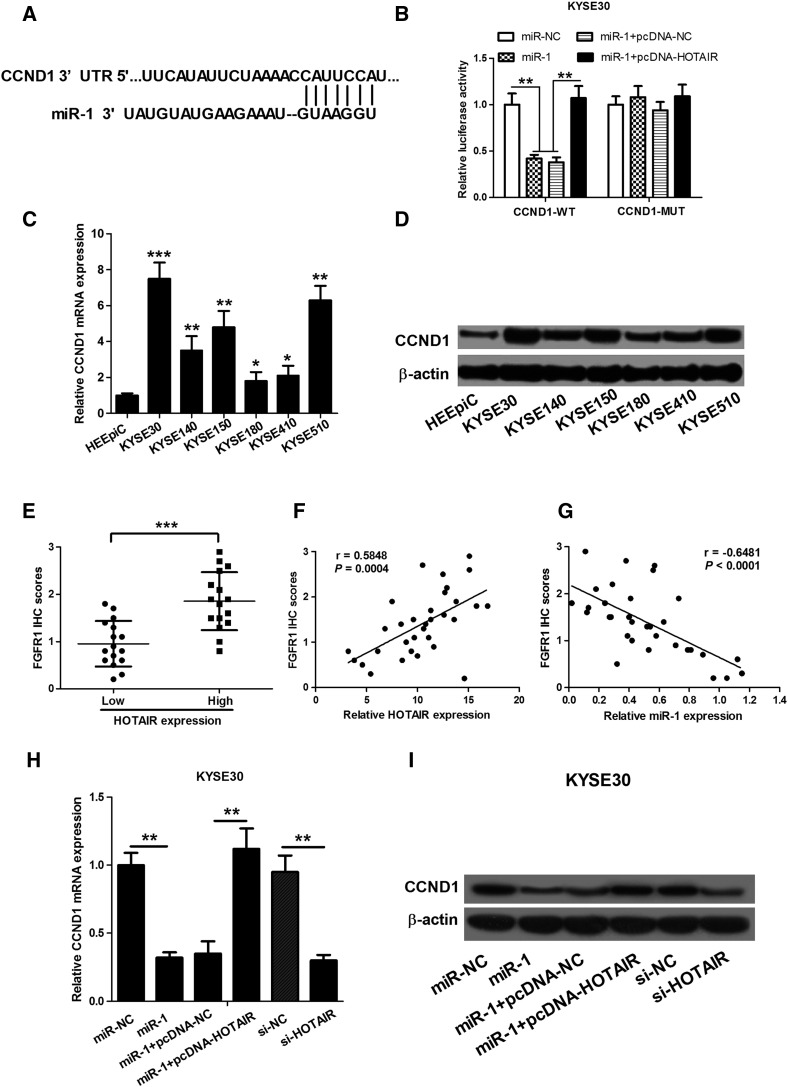
Figure 4.
HOTAIR works in ESCC cells by controlling the miR-1 target, CCND1. (A) Bioinformatics-based target prediction analysis shows that CCND1 is a potential target of miR-1. (B) Dual-luciferase reporter assay shows that the increase of miR-1 level reduces the luciferase activity of the pMIR luciferase reporter containing CCND1-WT, but not mutant reporter, and the treatment of miR-1 + pcDNA-HOTAIR restores the luciferase activity of the pMIR luciferase reporter containing CCND1-WT, but not mutant reporter, as compared with miR-1 and miR-1 + pcDNA-NC groups. (C and D) qRT-PCR and Western blot assay show that ESCC cells, especially KYSE30 and KYSE510 cells, have a higher level of CCND1 mRNA and protein than HEEpiC. (E) The immunohistochemistry shows that CCND1 levels in high-HOTAIR ESCC tissues were significantly higher than those in low-HOTAIR ESCC tissues. (F) The correlation analysis shows that CCND1 levels were positively correlated with HOTAIR expression in ESCC tissues. (G) The correlation analysis shows that CCND1 levels were inversely correlated with miR-1 expression in ESCC tissues. (H and I) Overexpression of miR-1 or knockdown of HOTAIR in KYSE30 cells markedly induces the expression of CCND1 mRNA and protein expression, and the treatment of miR-1 + pcDNA-HOTAIR regains the expression of CCND1 mRNA and protein. *P < .05, **P < .01, and ***P < .001.