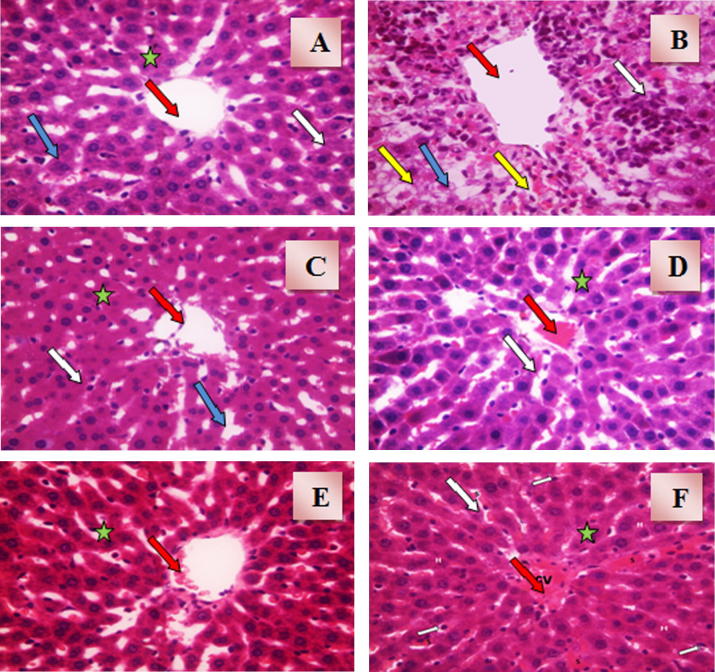
Figure 1.
(A) A photomicrograph of liver section obtained from control rats (H&E × 40). The section shows normal hepatic architecture with central vein (red arrow) and radiating cords of hepatocytes (star). Cords of hepatocytes are separated by blood sinusoids (blue arrow) lined with Kupffer cells (white arrow). (B) A photomicrograph of liver section obtained from acetaminophen hepatotoxicity control rats (H&E × 40). The section shows irregularly dilated central vein (red arrow) with massive inflammatory reactions and activated Kupffer cells (white arrow). Hepatocytes are showing cellular degeneration and centrilobular necrosis (yellow arrow). Hepatocytes are separated with dilated congested sinusoids (blue arrow). (C) A photomicrograph of liver section obtained from rats intoxicated with acetaminophen and pre-treated with N-acetylcysteine (H&E × 40). The section shows that all hepatocytes are normal with slightly congested central vein (red arrow). Hepatocytes are separated with slightly congested blood sinusoids (blue arrow) with some activated Kupffer cells (white arrow). (D) A photomicrograph of liver section obtained from rats intoxicated with acetaminophen and pre-treated with amlodipine (H&E × 40). The section shows that all hepatocytes (star) are normal with dilated congested central vein (red arrow) and activated Kupffer cells (white arrow). (E) A photomicrograph of liver section obtained from rats intoxicated with acetaminophen and pre-treated with lisinopril (H&E × 40). The section shows nearly normal architecture and normal hepatocytes (star) with minimal congested central vein (red arrow) and some activated Kupffer cells (white arrow). (F) A photomicrograph of liver section obtained from rats intoxicated with acetaminophen and pre-treated with allopurinol (H&E × 40). The section shows normal architecture and normal hepatocytes (star) with irregularly dilated congested central vein (red arrow) and some activated Kupffer cells (white arrow).