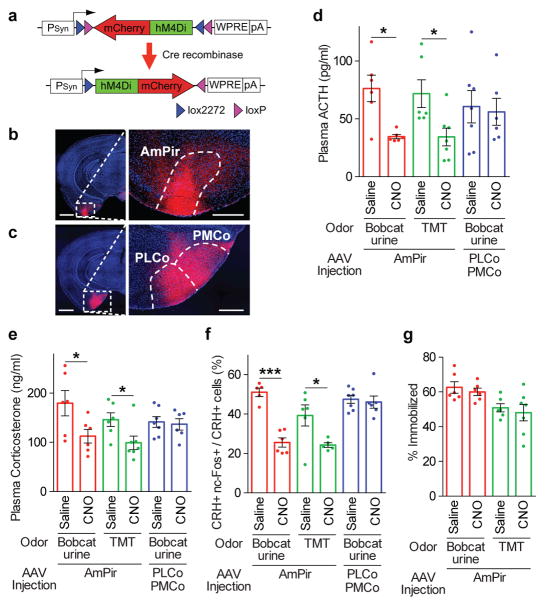
Figure 4. Chemogenetic silencing of AmPir inhibits stress hormone responses to predator odors.
a–c, mCherry immunostaining (red) after injection of AAV DIO-hM4Di-mCherry (a) into AmPir (b) or PLCo/PMCo (c). Scale bars, 1 mm (left), 400 μm (right).
d, e, Plasma ACTH (d) or corticosterone (e) concentration after mice expressing hM4Di in AmPir or PLCo/PMCo were injected with saline or CNO and then exposed to bobcat urine or TMT. (n=6–7 per condition. Error bars indicate SEM. *p<0.05. Mann-Whitney U test (d) or Unpaired t-test (e).)
f, Percentage of PVN CRH+ neurons expressing nc-Fos in animals treated as in (d, e). (n=5–7 per condition. Error bars indicate SEM. *p<0.05, ***p<0.001. Unpaired t-test.)
g, Animals expressing hM4Di in AmPir (d–f) were videotaped during exposure to bobcat urine and videos analyzed for the percentage of time spent immobile (% immobilized). (n=6–7 per condition. Error bars indicate SEM.)