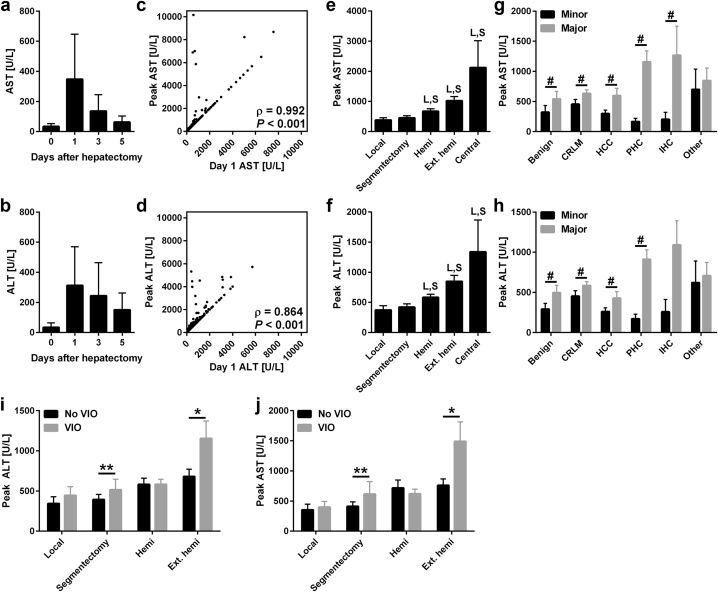
Figure 1.
Transaminase levels in relation to time, type of resection, diagnosis and vascular inflow occlusion. Postoperative AST (a) and ALT (b) levels before and 1, 3, and 5 days after hepatectomy. Data represent median ± IQR for N = 192–498 per time point. Panels c and d display the correlation of peak AST (c) and ALT (d) with day 1 values. Correlations were tested using Spearman's rank correlation coefficient for N = 539. Panels e and f display the peak AST (e) and ALT (f) according to the extent of resection. L indicates P < 0.05 versus the local resection group and S indicates P < 0.05 compared to the segmentectomy group. Data represent mean ± SEM for N = 4–149 per group. Panels g and h display peak AST (g) and ALT (h) diagnosis and major/minor resection. Data represent mean ± SEM for N = 4–97 per group. # indicates P < 0.05 between major and minor resections within diagnosis groups. Panels i and j demonstrate the peak ALT (i) and AST (j) levels according to the application of VIO in the different resection groups. Central liver resections were left out as N = 2 per group. Differences between groups were analyzed using Kruskal–Wallis or Mann–Whitney U tests. * indicates P < 0.05 and ** indicates P < 0.01. Abbreviations: AST, aspartate transaminase; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; hemi, hemihepatectomy; Ext. hemi, extended hemihepatectomy; CRLM, colorectal liver metastasis; HCC, hepatocellular carcinoma; PHC, perihilar cholangiocarcinoma; IHC, intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma