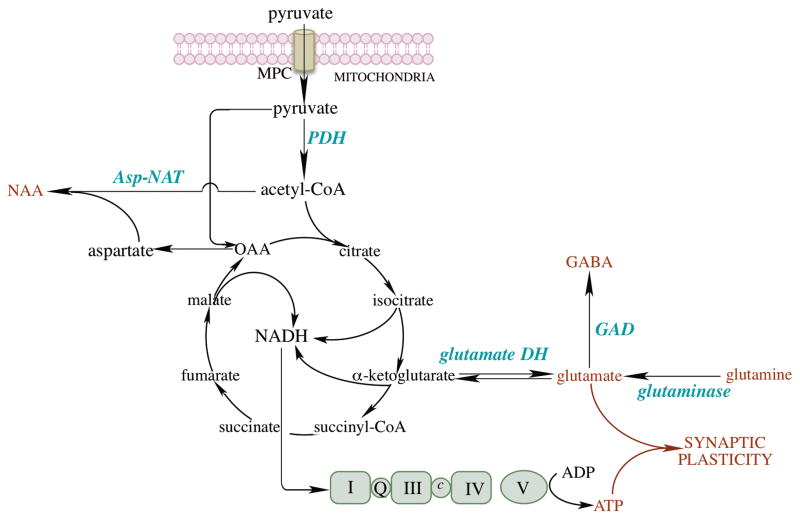
Fig. 3. Mitochondrial energy metabolism in brain.
Pyruvate imported by the mitochondrial pyruvate carrier (MPC) is converted to acetyl-CoA, which enters the TCA cycle to generate NADH, the reducing equivalents of which flow through the respiratory chain and oxidative phosphorylation. ATP generated by oxidative phosphorylation together with glutamate and GABA are critical for synaptic plasticity in brain. Glutamate is primarily generated from (a) α-ketoglutarate by glutamate dehydrogenase and (b) astrocyte-originated glutamine by glutaminase. GABA is produced by glutamate decarboxylase from glutamate. Acetyl-CoA is also a co-substrate for the synthesis of N-acetylaspartate (NAA) by aspartate N-acetyltransferase (Asp-NAT). Aspartate generated from oxaloacetate (coupled to the conversion of glutamate to α-ketoglutarate) is critical in cell proliferation.