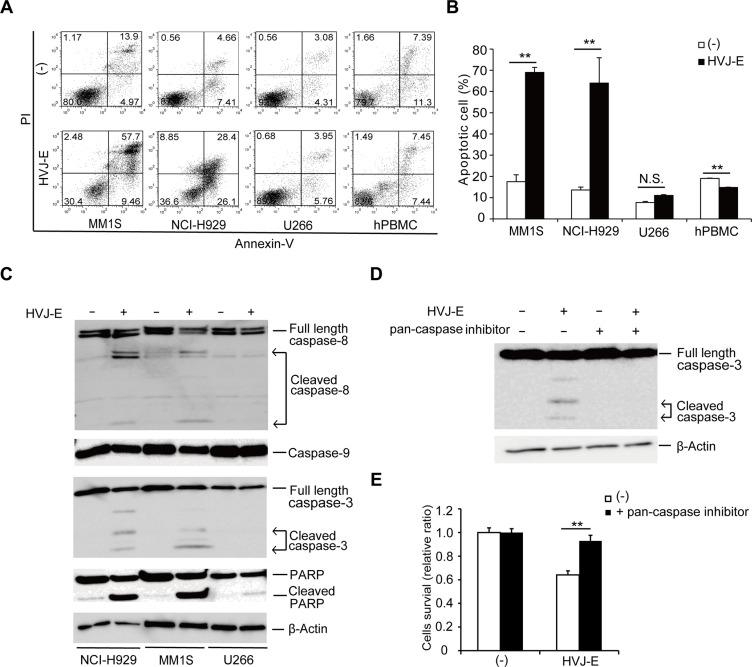
Figure 1. HVJ-E induces caspase-dependent apoptosis in MM cells.
(A) Apoptotic cells were measured in HVJ-E-treated NCI-H929, MM1S, U266 and PBMCs from healthy donors at a multiplicity of infection (MOI) of 1000 for 48 hours using PI (vertical) and Annexin V (horizontal) double staining analysis by FACS. (B) Quantification plot of the ratio of the apoptotic (Annexin V+) cells shown in Figure 1A. The data represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments (**P < 0.01, Student's unpaired t-test). (C) Detection of caspases (caspase-8, -3, -9) and poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase (PARP) in MM cells (NCI-H929, U266, MM1S) after treatment with HVJ-E at an MOI of 1000 for 48 hours by western blotting analysis. (D) Immunoblotting results for caspase-3 cleavage after HVJ-E treatment (1000 MOI, 24 hours) in the presence or absence of pan-caspase inhibitor in NCI-H929 cells. (E) NCI-H929 cells were treated with HVJ-E at an MOI of 1000 for 48 hours in the presence or absence of pan-caspase inhibitor, and cell viability was assessed using the MTS assay. The data represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments (**P < 0.01, Student's unpaired t-test).