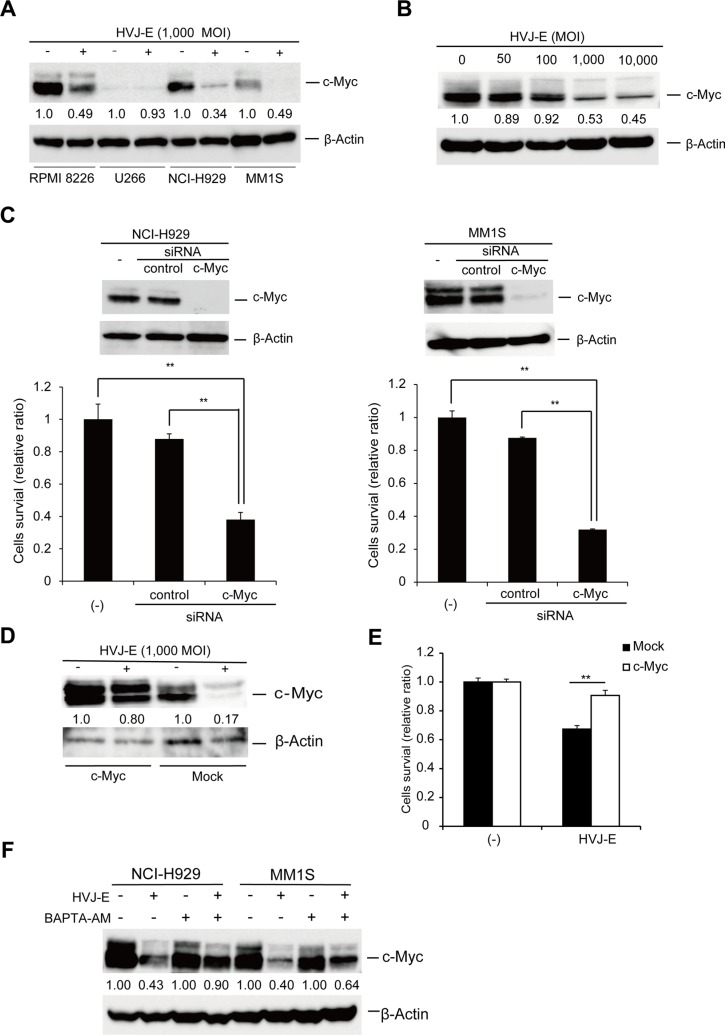
Figure 4. HVJ-E-induced apoptosis is associated with c-Myc downregulation.
(A) Immunoblotting study of c-Myc expression after HVJ-E treatment (1000 MOI, 24 hours) in MM cell lines (RPMI-8226, NCI-H929, U266, and MM1S). (B) Dose-dependent effects of HVJ-E treatment on c-Myc expression in NCI-H929. (C) c-Myc and expression were evaluated by immunoblotting analysis in untreated, control and c-Myc siRNA-transduced NCI-H929 and MM1S cell lines, Cell viability was measured using the MTS assay at 72 hours after the transduction of control or c-Myc siRNA into NCI-H929 and MM1S cells. The data represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments (**P < 0.01, Student's unpaired t-test). (D) Immunoblotting of whole-cell lysates from empty vector- or c-Myc expression vector-transduced MM1S cells after treatment with HVJ-E (1000 MOI, 24 hours). (E) Measurement of the cell viability of either empty or c-Myc-overexpressing MM1S cells treated with HVJ-E (1000 MOI, 36 hours) using the MTS assay. The data represent the mean ± SD of three independent experiments (**P < 0.01, Student's unpaired t-test). (F) Detection of c-Myc expression in NCI-H929 and MM1S cells after treatment with HVJ-E with or without BAPTA-AM for 20 hours by immunoblotting.