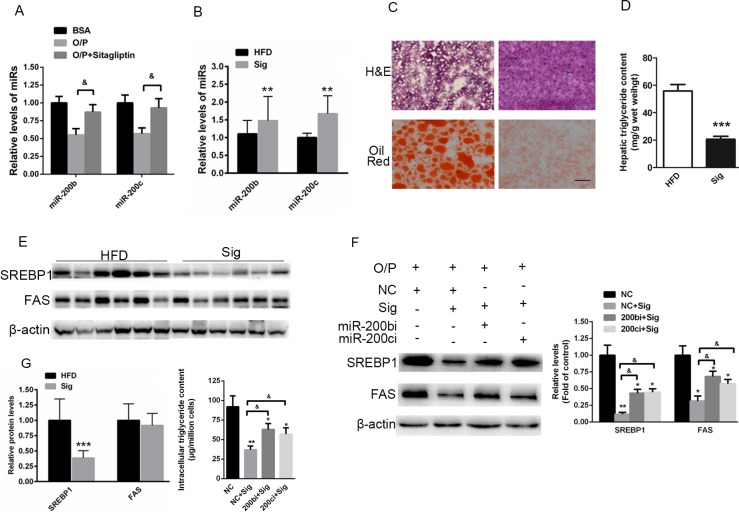
Figure 7. Elevated miR-200b and miR-200c expression is associated with sitagliptin-reduced hepatic lipid accumulation in mice fed a HFD.
(A) Real-time reverse-transcription PCR analysis of miR-200b and miR-200c expression in Hep1-6 cells pre-treated with a mixture of oleic acid/palmitic acid (2:1, M/M) for 24 h and then treated with 1 μM sitagliptin for 24 h. (B) Quantification of miR-200b and miR-200c in the livers of HFD-fed mice treated with sitagliptin. (C) Oil red O staining and H&E staining of the livers of HFD-fed mice treated with 3 mg/kg/day sitagliptin via i.g. for 8 weeks. (D) Measurement of hepatic triglyceride content in HFD-fed mice treated with sitagliptin. (E) Western blot analysis showing the expression of SREBP1 in the livers of sitagliptin-treated mice fed a HFD. (F, G) Western blot analysis showed that inhibition of miR-200b and miR-200c could partially rescue sitagliptin-induced reduced levels of SREBP1 and FAS, and decreased contents of intracellular triglyceride in Hep1-6 cells. The data represent the mean ± SEM, n = 6 mice or n = 3 independent experiments. *P < 0.05 and **P < 0.01 versus the control; & P < 0.05 versus NC+Sig. The bar represents 25 μm.