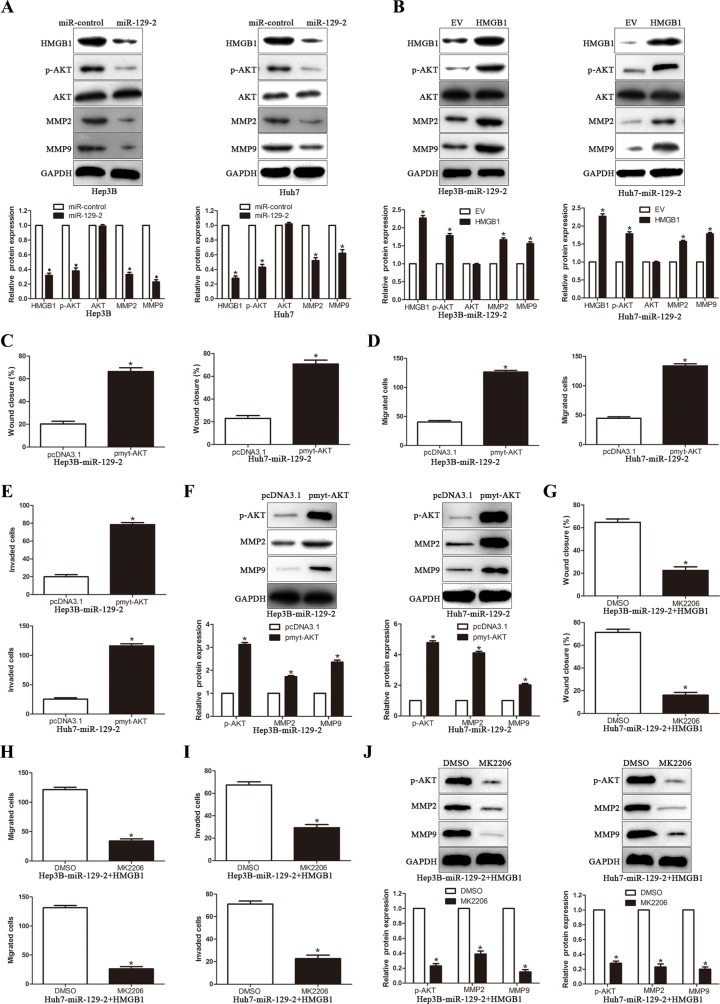
Figure 6. miR-129-2-HMGB1 axis modulates the expression of MMP2 and MMP9 by inhibiting AKT phosphorylation.
(A) Western blot analysis showing decreased levels of p-AKT, MMP2/9 in miR-129-2–overexpressed Hep3B and Huh7 cells. (B) Western blot analysis for AKT/p-AKT, MMP2/9 protein expression in miR-129-2-overexpressing Hep3B and Huh7 cells following transfection with HMGB1 plasmid.(C-F) The miR-129-2-overexpressing Hep3B and Huh7 cells were transiently transfected with pmyt-AKT to increase the expression of p-AKT. The cells were subjected to wound healing assay (C) and Transwell migration assay (D) and the Matrigel invasion assay (E) to detect the functional effect and Western blot (F) to investigate the expression of MMP2/9. p-AKT overexpression abrogated the suppressive effects of miR-129-2 overexpressed on HCC cells. (G–J) The HMGB1 rescue experiment that co-transfection of HMGB1 in miR-129-2-overexpressing Hep3B and Huh7 cells, were treated with AKT inhibitors, MK2206 (2 μmol/L). Then the capacity of cell migration (G, wound healing assay and H, Transwell migration assay) and cell invasion (I, Matrigel invasion assay), the MMP2/9 expression was determined by Western blot (J). p-AKT inhibitor abolished the HMGB1 rescue experiment on the functional effects and the expression of MMP2/9. n = 6 independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.