Figure 3. ISX enhances E2F1 expression and nuclear translocation.
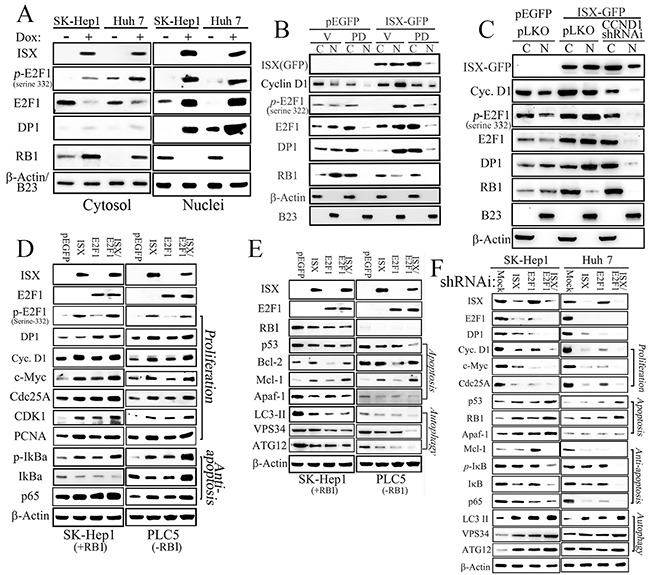
A. ISX induces the expression of p-E2F1 (serine 332) and DP1 in the nucleus. B. A cyclin D1–CDK4/6 inhibitor, PD 0332991 (PD; 30 nM) reduced the expression of E2F1 and p-E2F1 in the nucleus in response to ISX-GFP. C, cytoplasm; N, nuclei. C. The hepatoma cells transfected with cyclin D1-specific shRNAi decreased the expressions of p-E2F1, E2F1, DP-1, and RB1 in the nucleus in response to ISX-GFP. D. Expressions of various proliferation and anti-apoptosis related proteins in cells [SK-Hep1 (RB1+) and PLC5 (RB1−)] transfected with ISX and/or E2F1 genes. E. Forced coexpression of ISX and E2F1 inhibits apoptotic and autophagic signaling in SK-Hep1 (RB1+) and PLC5 (RB1−) cells. F. Hepatoma cells (SK-Hep1 and Huh 7) cotransfected with ISX and E2F1 shRNAi showed dramatically decreased proliferation and anti-apoptotic signals but increased apoptotic and autophagic signals from those in the cells transfected with ISX or E2F1 shRNAi alone. Assays were performed three times.
