Figure 1. PKCδ localizes at the cell-cell contacts through its C2-like domain in an F-actin-dependent manner.
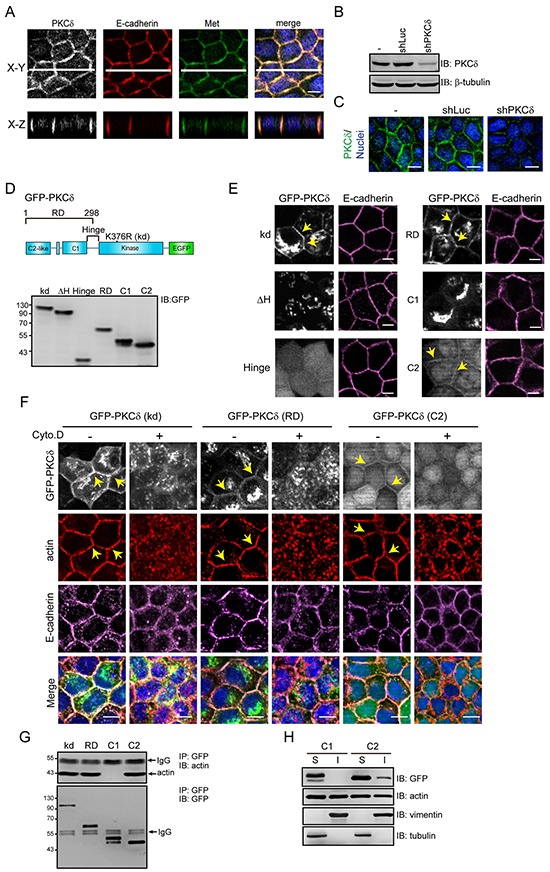
A. MDCK cells were grown to confluence and were then stained for PKCδ, E-cadherin, Met, and DNA. White lines on the confocal x-y sections represent regions where the confocal x-z sections were taken. The scale bar represents 10 μm. B. MDCK cells were infected with recombinant lentiviruses expressing shRNA specific to canine PKCδ (shPKCδ) or to luciferase (shLuc) as a control. The expression levels of PKCδ and β-tubulin (as a loading control) were analyzed by immunoblotting (IB) with the indicated antibodies. C. The cells, as in panel (B), were stained for PKCδ and DNA. The scale bar represents 10 μm. D. The diagram depicts the domain organization of GFP-PKCδ. The GFP-PKCδ derivatives including the kinase-deficient mutant (kd; K376R), the ΔH mutant with a deletion of the hinge region (a.a. 280-347), the regulatory domain (RD; a.a. 1-298), the C2-like domain (C2; a.a. 1-123), the C1 domain (C1; a.a. 124-298), and the hinge region (a.a. 280-347) were stably expressed in MDCK cells. The expression levels of the GFP-PKCδ derivatives were analyzed by immunoblotting with anti-GFP antibody. E. The cells, as in panel (D), were stained with anti-E-cadherin antibody (clone ECCD2). The arrowheads indicate the presence of the GFP-PKCδ kd mutant, the regulatory domain, and the C2-like domain at the cell-cell contacts. The scale bar represents 10 μm. F. MDCK cells stably expressing GFP-PKCδ kd mutant, RD, or C2-like domain, were grown to confluence and were then treated with 10 μM cytochalasin D (Cyto. D) for 2 h before they were stained with anti-E-cadherin (clone 36), anti-actin, and DAPI. The arrows indicate the presence of the GFP-PKCδ proteins and F-actin at the cell-cell contacts. The scale bar represents 10 μm. G. MDCK cells stably expressing GFP-PKCδ proteins (kd, RD, C1, and C2-like) were grown to confluence before they were lysed. The GFP-PKCδ proteins were immunoprecipiated (IP) by anti-GFP antibody and the immunocomplexes were analyzed by immunoblotting (IB) with antibodies to actin and GFP. H. MDCK cells stably expressing GFP-PKCδ C1 domain or C2-like domain were grown to confluence. The cell lysates were fractionated into 1% NP40-soluble (S) and insoluble (I) fractions and analyzed by immunoblotting with the indicated antibodies.
