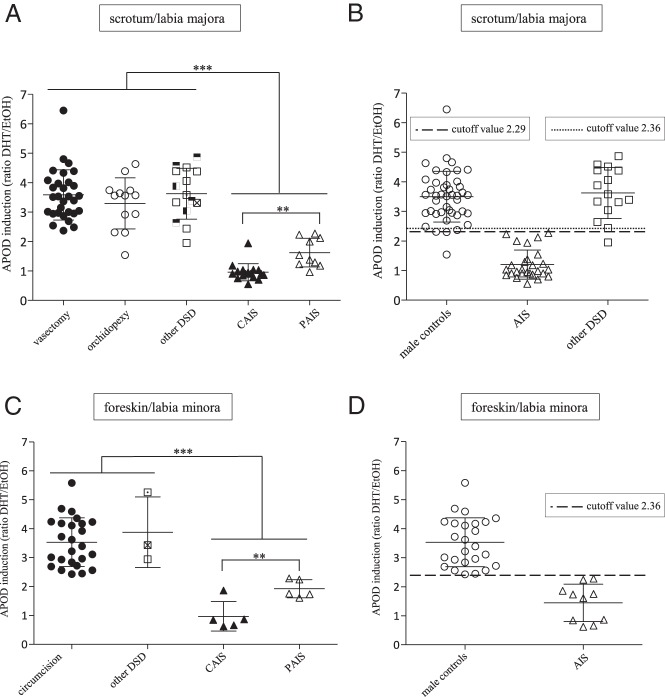
Figure 2.
DHT-dependent, AR-induced APOD mRNA expression represented as the ratio between ethanol (EtOH)- and DHT-treated GFs. A, Scrotum-derived male controls (vasectomy, orchidopexy [group 1]), labioscrotal derived molecular defined DSDs (other DSDs [group 2]), and AR-CDS mutation-positive AIS (CAIS, PAIS [group 3]). B, Depiction of cutoff values between male controls (vasectomy and orchidopexy) and AR-CDS mutation-positive AIS (CAIS and PAIS) of 2.29 (100% sensitivity, 97.7% specificity, P < .0001) and between the same AR-CDS mutation-positive AIS and molecular defined DSDs (other DSDs) of 2.36 (100% sensitivity, 93,3% specificity, P < .0001). C, Foreskin-derived male controls (circumcision [group 1]) and molecular-defined DSDs (other DSDs [group 2[) as well as AR-CDS mutation-positive AIS (CAIS, PAIS [group 3]). D, Depiction of the cutoff value between male controls (circumcision) and AR-CDS mutation-positive AIS (CAIS and PAIS) of 2.36 (100% sensitivity, 100% specificity, P < .0001). Means and SDs are included as error bars. Values of P < .001 are denoted by three stars, and those values of P < .01 are denoted by two stars. Among the DSD diagnoses other than AIS, empty squares represent SRD5A2, horizontally half-filled squares represent HSD17B3, vertically half-filled squares represent CYP17A1, crossed squares represent CYP21A2, and dotted squares represent NR5A1 mutations.