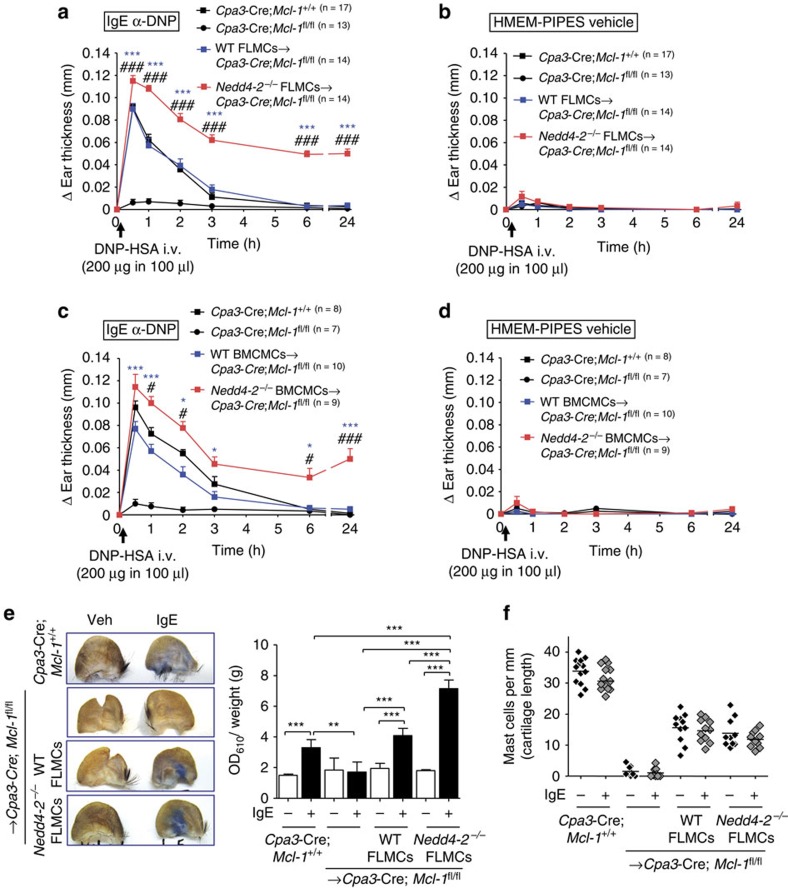
Figure 2. Mast cell–Nedd4-2 restrains IgE-mediated passive cutaneous anaphylaxis.
Changes (Δ) in ear thickness 0–24 h after i.v. injection of DNP–HSA (200 μg in 100 μl) into mice, with DNP–HSA given 16 h after i.d. injection of anti-DNP IgE (SPE-7, 100 ng) in the right ear pinna (a,c) and equal volume of HMEM-Pipes vehicle in the left ear pinna (b,d) of Cpa3-Cre; Mcl-1+/+ (filled black squares), mast cell-deficient Cpa3-Cre; Mcl-1fl/fl (filled black circles), and mast cell-deficient mice engrafted i.d. with (a,b) WT FLMCs (WT FLMCs→Cpa3-Cre; Mcl-1fl/fl, filled blue squares) or Nedd4-2−/− FLMCs (Nedd4-2−/− FLMCs→Cpa3-Cre; Mcl-1fl/fl, filled red squares), and (c,d) WT BMCMCs→Cpa3-Cre; Mcl-1fl/fl (filled blue squares) or Nedd4-2−/− BMCMCs→Cpa3-Cre; Mcl-1fl/fl (filled red squares) mice. Data (mean±s.e.m.) are pooled from the four (a,b) or three (c,d) independent experiments performed, each of which gave similar results, each with 3–5 mice per group. *P<0.05, ***P<0.001 for comparisons of WT MCs versus Nedd4-2−/− MCs→Cpa3-Cre; Mcl-1fl/fl mice. #P<0.05, ###P<0.001 for comparisons of WT mice versus Nedd4-2−/− MCs→Cpa3-Cre; Mcl-1fl/fl mice (two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) with Bonferroni post test). (e) Evans blue dye extravasation (weight adjusted) quantified by absorption at 610 nm in vehicle or IgE anti-DNP treated ear pinnae at 30 min after i.v. (tail vein) DNP–HSA (containing Evans blue dye) administration. Representative ears shown for each group of mice tested. Data (mean±s.d.) are from one experiment with 4–5 mice per group. **P<0.01, ***P<0.001 for indicated comparisons (one-way ANOVA with Bonferroni post test); (f) Dermal mast cell numbers in ear pinnae of mice at the completion of three of the PCA experiments (that is, at 24 h after injection of DNP–HSA) outlined in (a,b).