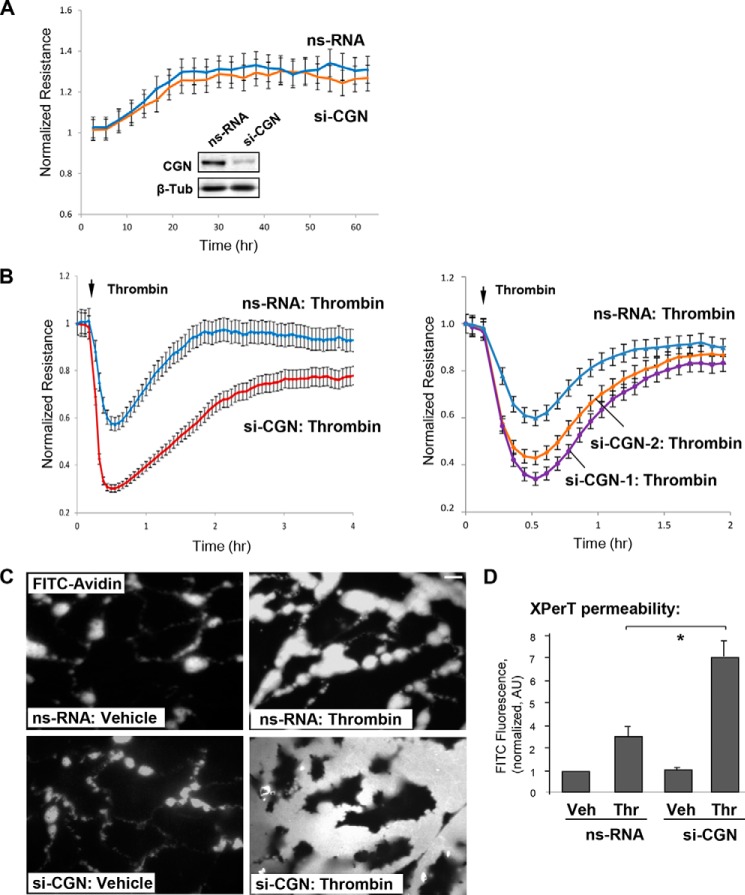
FIGURE 1.
Cingulin knockdown exacerbates thrombin-induced EC hyperpermeability. Human lung ECs were transfected with a 200 nm pool of four cingulin-specific siRNAs (si-CGN), two single cingulin-specific siRNAs (si-CGN1 and si-CGN2), or nonspecific (ns) RNA. A, measurements of TER were performed in unstimulated ECs over time. siRNA-induced cingulin protein depletion was confirmed by Western blotting. B, at the time point indicated by the arrow, control or cingulin-depleted ECs were stimulated by thrombin (0.1 unit/ml), and TER measurements were performed over time. Results are representative of four independent experiments. C and D, cells grown on glass coverslips (C) or 96-well plates (D) with immobilized biotinylated gelatin (0.25 mg/ml) were stimulated with vehicle (Veh) or thrombin (Thr) for 10 min followed by addition of FITC-avidin (25 μg/ml, 3 min). Unbound FITC-avidin was removed, and FITC fluorescence signal was visualized by fluorescence microscopy; bar, 5 μm (C). Alternatively, fluorimetric analysis of the FITC fluorescence signal in control and agonist-stimulated ECs plated in 96-well microplates was performed using the Victor X5 multilabel plate reader (see “Experimental Procedures”). Normalized data are expressed as means ± S.D.; n = 5, *, p < 0.05 (D). AU, arbitrary units.