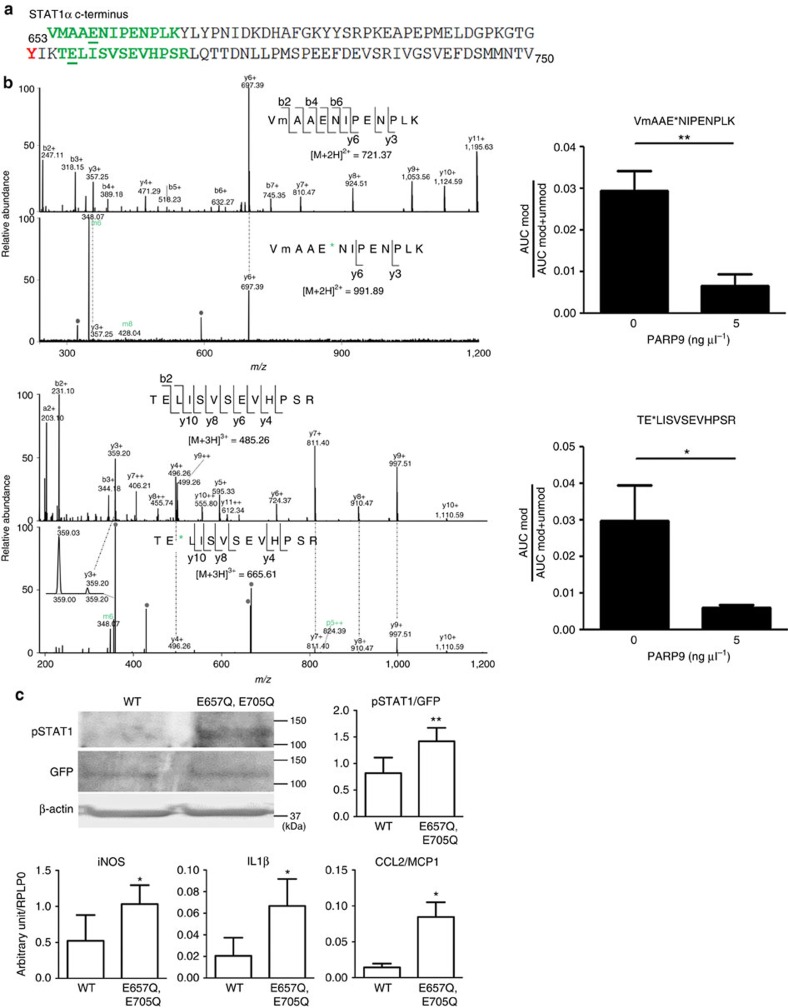
Figure 6. Identification of PARP14-induced ribosylation sites in STAT1.
(a) The amino-acid sequence of human STAT1α C terminus. Green amino acids indicate ribosylated peptides; confirmed ribosylation sites are underlined. STAT1 is phosphorylated at indicated tyrosine (red). (b; Left panels) MS/MS spectra for the mono-ADP-ribosylated peptides and corresponding unmodified forms. ADP-ribose fragments are annotated in green. *, ribosylation site; m, oxidized methionine. The grey circles indicate background or undetermined ions. (Right panels) MS1-based quantification of PARP9 inhibition of PARP14-mediated STAT1α ribosylation at E657 (upper panel) and E705 (lower panel), respectively. (c) Effects of mutated amino acids at E657 and E705 in STAT1 (ribosylation sites for PARP14) on its Tyr701 phosphorylation and pro-inflammatory gene expression in mouse bone marrow-derived macrophages (n=4). *P<0.05 and **P<0.01, respectively, by Student's t-test. Error bars indicate s.d.