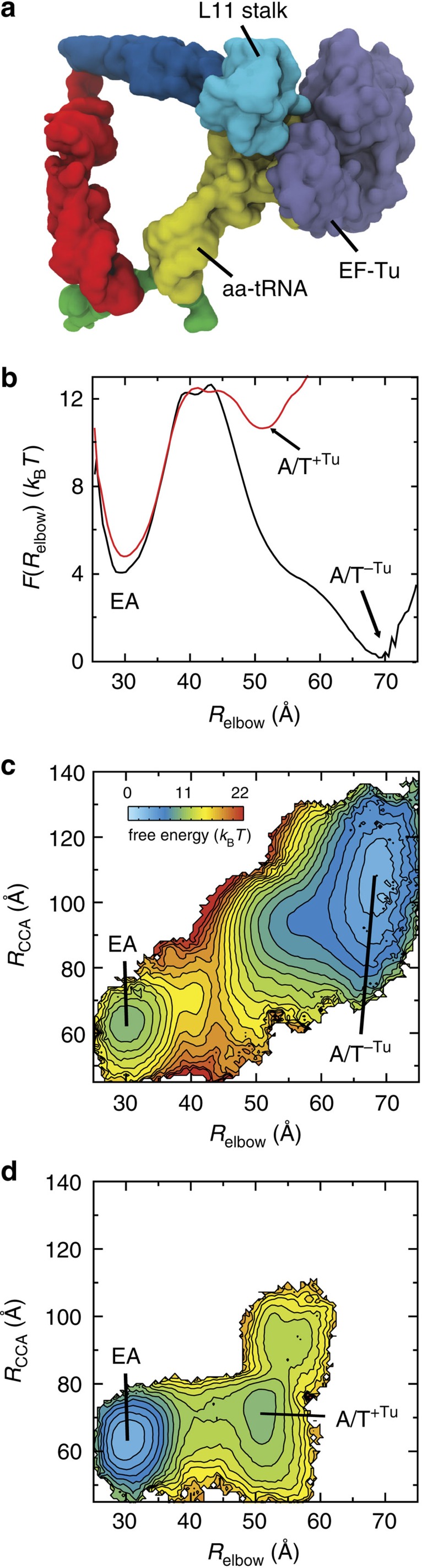
Figure 2. EF-Tu occludes access of aa-tRNA to A/T-like conformations.
(a) EF-Tu, in the form of ternary complex (EF-Tu̇GTṖaa-tRNA), binds the ribosome at the opening of the accommodation corridor20,21,22,23,24,26,29. (b) When EF-Tu is restrained to its GTP conformation on the ribosome, and a minimal affinity for aa-tRNA is included, the barrier to elbow accommodation is reduced by ∼10 kBT (red curve), relative to the barrier when EF-Tu is absent (black curve). (c,d) Two-dimensional free-energy profiles, calculated for the models that lack EF-Tu (c) and include EF-Tu (d). There is a drastic reduction in the range of accessible conformations of aa-tRNA when EF-Tu is bound to the ribosome. This leads to destabilization, and shift in position, of the A/T-like ensemble (A/T−Tu in c and A/T+Tu in d).