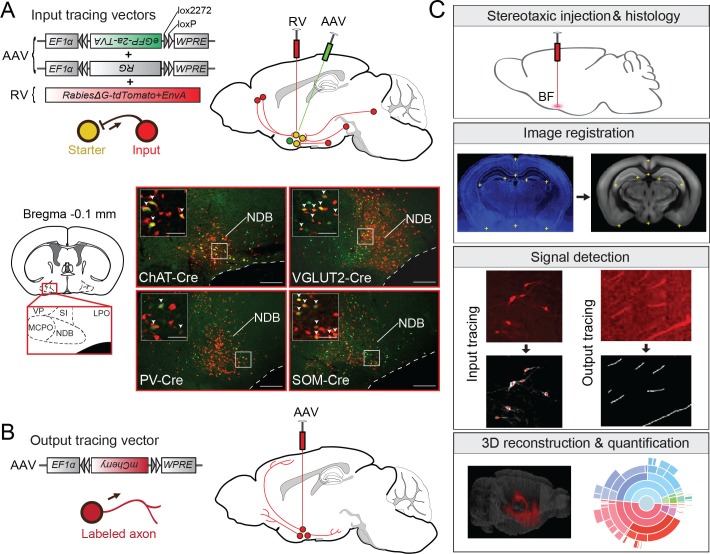
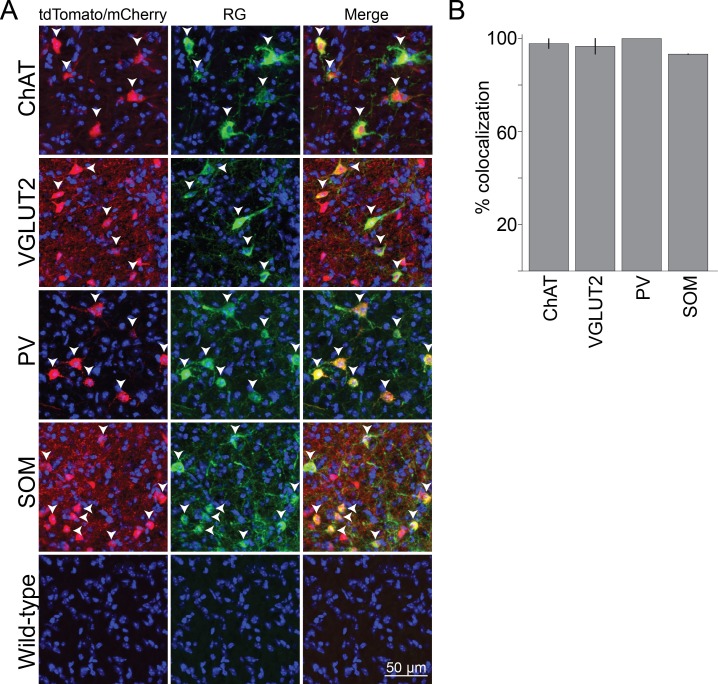
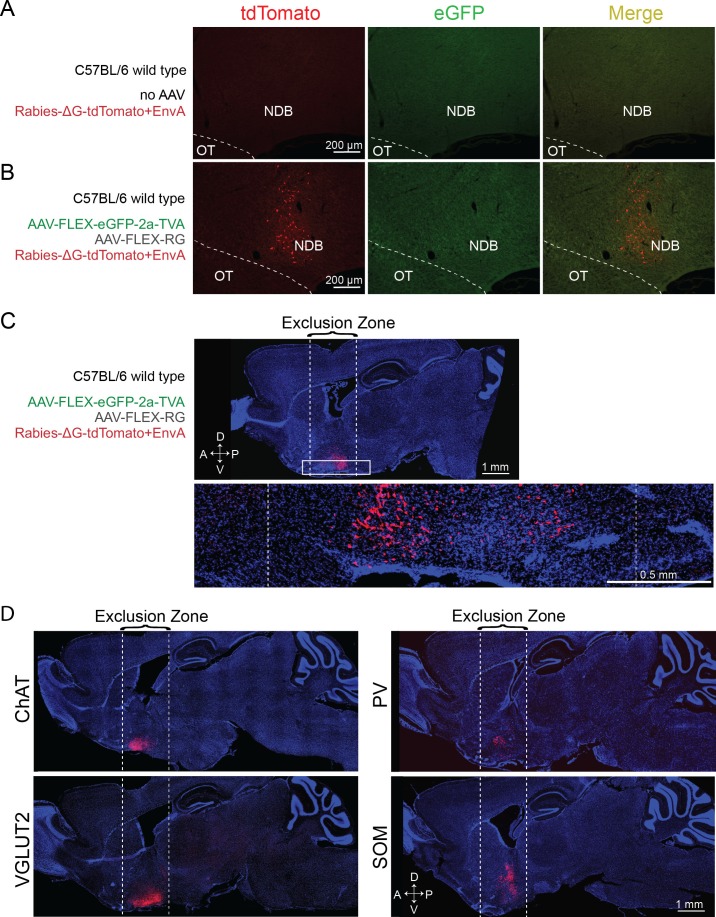
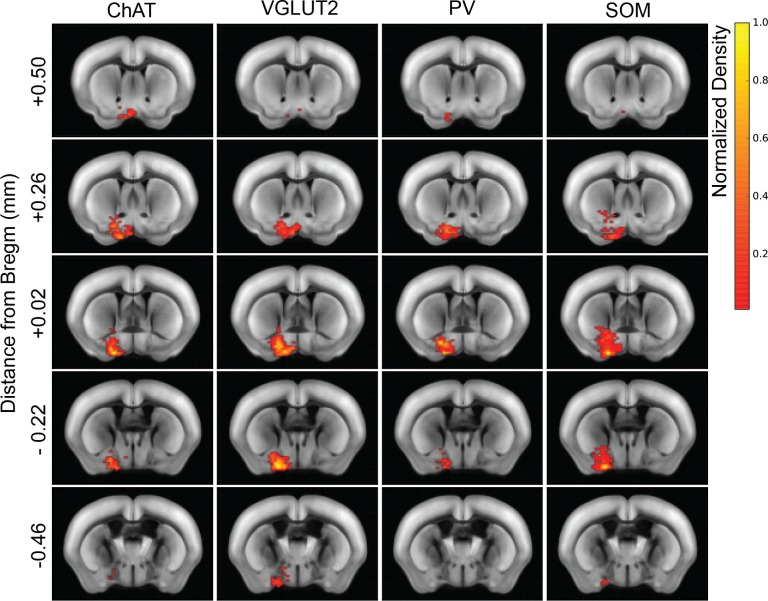
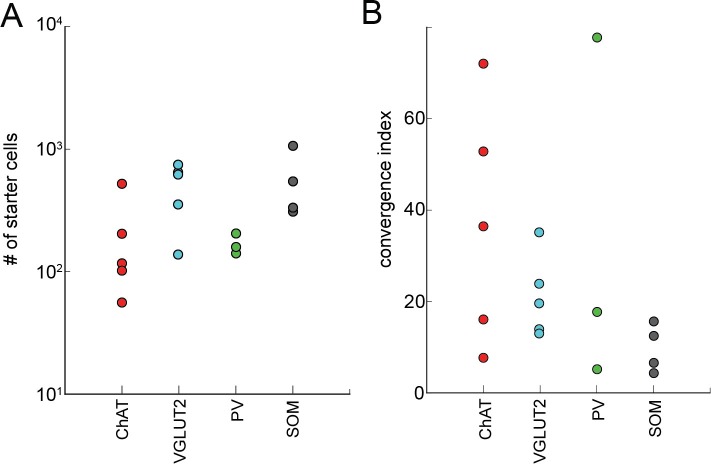
Figure 1. Experimental and analysis procedures for cell-type-specific circuit tracing.
(A) RV-mediated transsynaptic retrograde tracing of BF inputs. Upper panel, viral vectors and injection procedure. Lower panel, fluorescence images of BF in the region of the NDB (red box in coronal diagram) in ChAT-, VGLUT2-, PV-, and SOM-Cre mice. Scale bar, 200 µm. Inset, enlarged view of the region in white box showing starter cells (yellow, expressing both eGFP and tdTomato, indicated by white arrowheads). Scale bar, 50 µm. NDB, diagonal band nucleus; SIB, substantia innominata, basal part; MCPO, magnocellular preoptic nucleus; VP, ventral pallidum; LPO, lateral preoptic area. (B) Viral vector and injection procedure for tracing BF axonal projections. (C) Flow chart showing the main steps in data generation and processing.
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.7554/eLife.13214.002
© 2008 Elsevier. All Rights Reserved
Lower panel, brain outline adapted from Figure 32 from The Mouse Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 3rd edition, Franklin, K.B.J. and Paxinos, G.