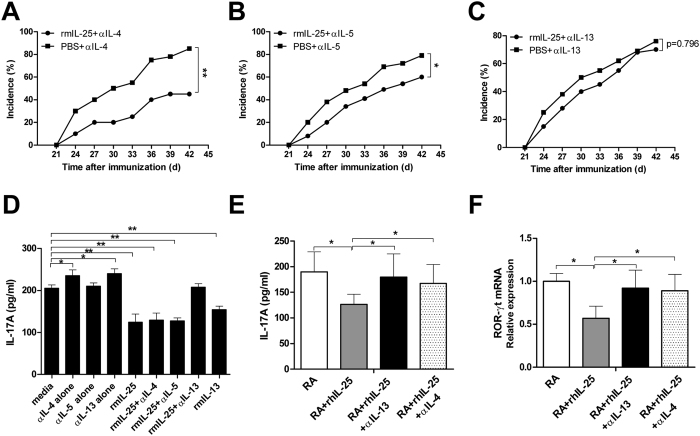
Figure 6. IL-25-mediated protection from CIA and Th17 suppression is IL-13 dependent.
Male DBA/1 mice were immunized with CII to induce arthritis, and received rmIL-25 (1 μg/mice) or PBS for 5 consecutive days beginning on day 1 after the second immunization with CII, The mice were injected with anti-IL-4, IL-5 or IL-13 blocking monoclonal antibody (mAb) on day 3 before (−3d) and day 3 (+3d) after the second immunization with CII. Incidence of CIA in mice treated with anti-IL-4 (A), anti-IL-5 (B), and anti-IL-13 (C) (n = 8 per group). Spleen CD4+ T cells were isolated from CIA mice and stimulated with plate-bound anti-CD3 (5 μg/mL) plus anti-CD28 (2 μg/mL) in the presence or absence of rm IL-25 (100 ng/mL) for 24 h. anti-IL-4 mAb (10 μg/mL), anti-IL-5 mAb (10 μg/mL), anti-IL-13 mAb (10 μg/mL) or rmIL-13 (100 ng/ml) were added at the start of the culture. IL-17A (D) levels in supernatant were assessed by ELISA. CD4+ T cells from PBMCs of RA patients were isolated and stimulated with anti-CD3 (5 μg/mL) plus anti-CD28 (2 μg/mL) in the presence or absence of rhIL-25 (100 ng/mL) for 24 h. anti-IL-13 mAb (10 μg/mL) or anti-IL-4 mAb (10 μg/mL) was added at the start of the culture. IL-17A (E) levels in supernatant were assessed by ELISA. The mRNA levels of ROR-γt (F) was detected by real-time PCR. Data are presented as the mean ± SEM of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.