Figure 5.
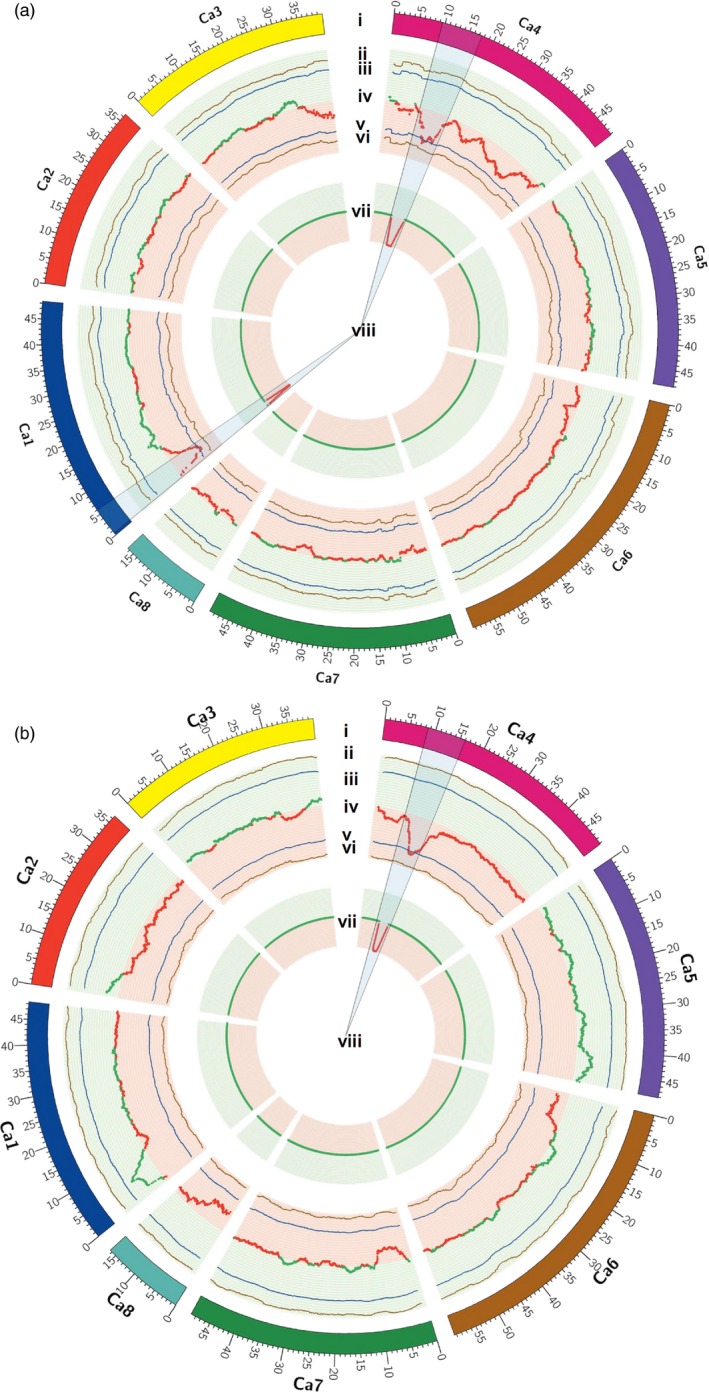
Co‐localization of QTLs from traditional and QTL‐seq approach for 100SDW and RTR. (a) Co‐localization of QTLs mapped for 100SDW through traditional and QTL‐seq method. (i) Psuedomolecules of reference genome CDC Frontier (Varshney et al., 2013), (ii) upper probability values at 99% confidence (P < 0.01), (iii) upper probability values at 95% confidence (P < 0.05), (iv) genomewide ΔSNP‐index [red dots denote ΔSNP‐index ranged from 0 to −1 and contributed by high trait parent (ICC 4958) and green dots denote ΔSNP‐index ranged from 0 to 1 and contributed by low trait parent (ICC 1882)], (v) lower probability values at 95% confidence (P < 0.05), (vi) lower probability values at 99% confidence (P < 0.01), (vii) physical position of earlier mapped QTL (Varshney et al., 2014a) for 100SDW through traditional mapping approach. The physical positions of QTL were estimated through blast of the flanking primers to the chickpea genome. (viii) Common genomic positions on linkage group 1 (CaLG01) and linkage group 4 (CaLG04) were observed through both the approaches. (b) Co‐localization of QTLs mapped for RTR through traditional and QTL‐seq method. (i) Psuedomolecules of reference genome CDC Frontier (Varshney et al., 2013), (ii) upper probability values at 99% confidence (P < 0.01) for declaring significant ΔSNP‐index, (iii) upper probability values at 95% confidence (P < 0.05) for declaring significant ΔSNP‐index, (iv) genomewide ΔSNP‐index [red dots denote ΔSNP‐index ranged from 0 to −1 and contributed by high trait parent (ICC 4958) and green dots denote ΔSNP‐index ranged from 0 to 1 and contributed by low trait parent (ICC 1882)], (v) lower probability values at 95% confidence (P < 0.05), (vi) lower probability values at 99% confidence (P < 0.01), (vii) physical position of earlier mapped QTL (Varshney et al., 2014a) for RTR through traditional mapping approach. The physical position of QTL was estimated through blast the flanking primers into the chickpea genome. (viii) Common genomic positions on CaLG04 were observed through both the approaches.
