Figure 2.
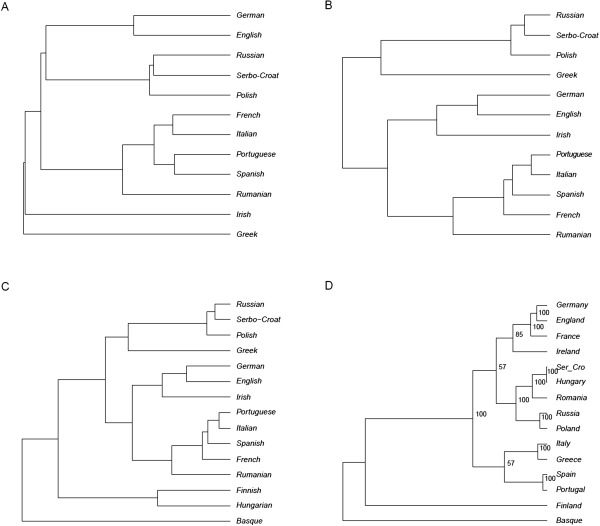
UPGMA trees summarizing population relationships. Distances inferred from: (A) lexical and (B) syntactic comparisons among 12 Indo‐European‐speaking European populations; (C) syntactic comparisons among 15 European languages, and (D) F ST distances among 15 populations sharing 177,949 SNPs. Lexical distances were estimated from lists of cognate words, amounting to over 6,000 roots (http://ielex.mpi.nl/); syntactic distances were measured over 56 parameters of nominal phrases (http://dx.doi.org/10.1075/jhl.3.1.07lon.additional). In (D), numbers indicate the support of the branching after 100 bootstrap replicates. The matrix perturbation techniques usable to test the robustness of trees (bootstrapping and jackknifing) provide stable topologies, but owing to the small number of characters involved they are only relatively reliable (cf. Longobardi et al., 2013 for more details). Therefore, bootstrapping scores have been only reported here for the genetic tree D.
