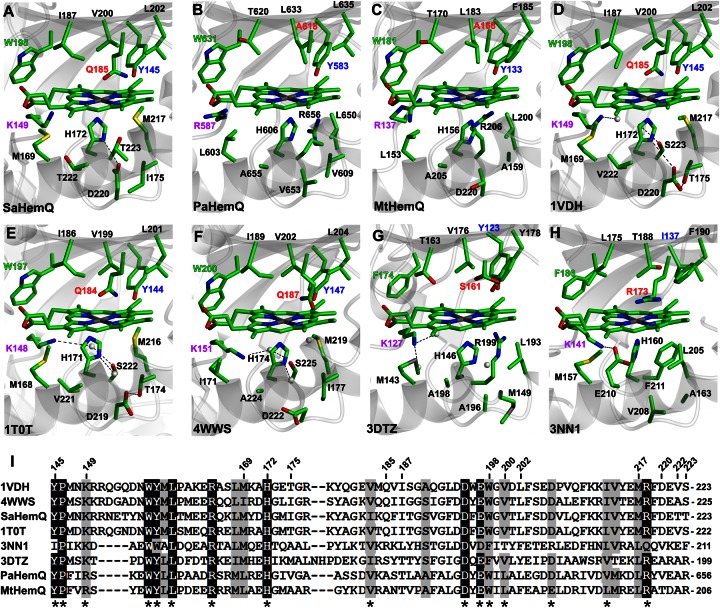
Figure 7. Structral analysis of the haem-binding cleft of HemQ family members.
Structural models of haem-binding clefts for HemQ enzymes from S. aureus (A, SaHemQ), P. acnes (B, PaHemQ), and M. tuberculosis (C, MtHemQ) were produced using the haem cofactor from the chlorite dismutase from Candidatus Nitrospira defluvii (H, 3NN1 [34]). (D–G) Apoprotein crystal structures of HemQ enzymes from T. thermophilus (1VDH [33]), B. stearothermophilus (1T0T), L. monocytogenes (4WWS [18]), and T. acidophilum (3DTZ), all with the haem cofactor from 3NN1 superimposed. (I) Multiple sequence alignment of sections of the proteins described above with residue numbers for SaHemQ marked at the top and functionally conserved residues marked with an asterisk.