Fig. 3.
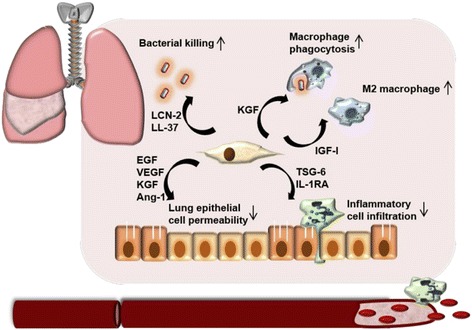
Mechanisms involved in MSC therapy for inflammatory pulmonary diseases based on preclinical animal studies. Immunomodulatory effects include enhancing bacterial clearance by direct killing and enhancement of macrophage phagocytosis; decreasing inflammatory response by modulation of macrophages towards an M2 phenotype and inhibition of neutrophil recruitment; as well as reducing damage to alveolar epithelium
