Scheme 2.
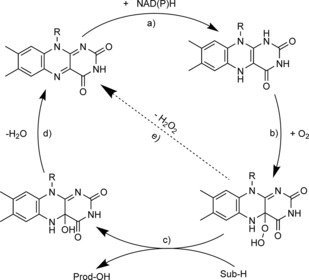
Simplified mechanism of flavin‐dependent monooxygenases, consisting of a) NAD(P)H‐dependent reduction of the flavin prosthetic group, followed by b) activation of molecular oxygen as a (hydro)peroxyflavin, and c) substrate oxygenation. The catalytic cycle is closed after d) elimination of water and reformation of the oxidised flavin. Alternatively, e) the (hydro)peroxyflavin can eliminate H2O2 spontaneously (uncoupling reaction).
