Scheme 4.
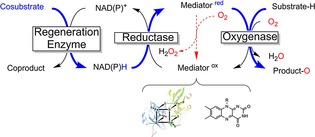
Simplified molecular architecture of multicomponent monooxygenases that are not directly dependent on NAD(P)H. Blue: path of reducing equivalents. NAD(P)H serves as a general reductant, transferring its reducing equivalents to a mediator molecule (either a flavin or an iron–sulfur cluster protein) with catalysis by a reductase. The usually protein‐based mediator delivers the reducing equivalents to the monooxygenase subunit for productive oxygen activation. However, direct reaction of the reduced mediator with O2 leads to futile reoxidation and (eventually) H2O2 formation.
