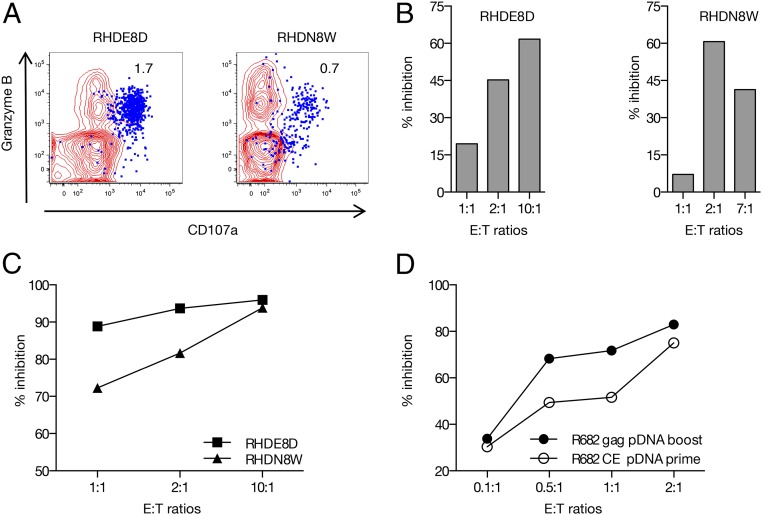
FIGURE 8.
CE-specific cytotoxic T cells reduce viral replication. (A) Plot overlays show the granzyme B content and degranulation activity (CD107a+) of the CE-specific T cells (in blue) upon peptide stimulation. Numbers within the plots indicate the percentage of IFN-γ+ T cells. (B) Inhibition of SIV replication (in percent of the negative control samples) measuring p27Gag in the culture supernatants in the presence of increasing amounts of CD8+ T cells from two representative macaques after the last p27CE+gag booster vaccination. (C) Reduction in the frequency of SIV infected cells by increasing amounts of autologous CD8+ T cells (collected after the last vaccination from RHDE8D and RHDN8W) as measured by intracellular p27Gag staining followed by flow cytometry. (D) Reduction in the frequency of SIV infected cells by increasing amounts of autologous CD8+ T cells, collected after CE pDNA prime (open circles) and gag pDNA (solid circles) from macaque R682, and measured as in (C).