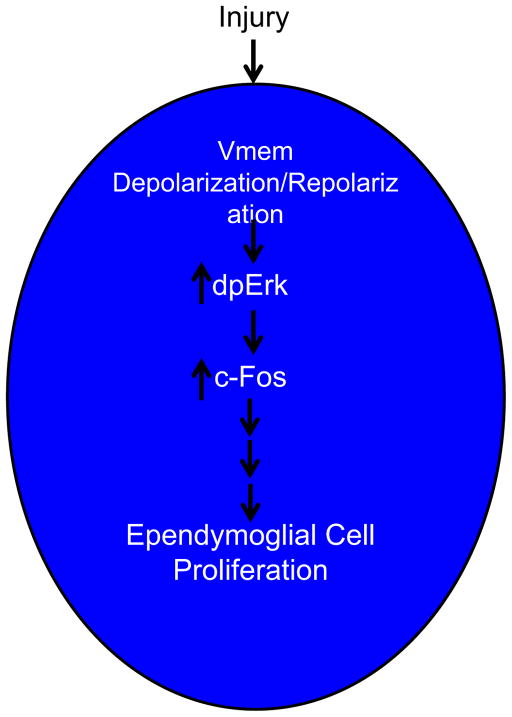
Fig. 10.
Schematic diagram of ependymoglial response to Injury. After injury to the spinal cord the membranes of the ependymal glial cells rostral and caudal to the injury site under go a rapid (7 h) depolarization and repolarization (24 h). This transient depolarization event is essential to activate genes expression cascades that are to initiate a pro-regenerative response. We identified one of these genes c-Fos, whose activation is inhibited by maintaining cells is a prolonged state of membrane depolarization, this subsequently inhibits regeneration.