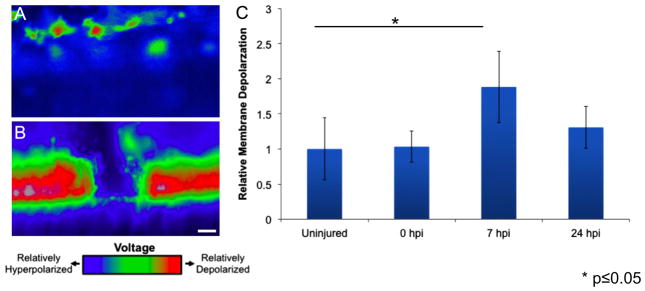
Fig. 3.
Spinal cord injury induces rapid but transient membrane depolarization. Animals were injected with the Vmem sensitive dye DiBAC and were imaged before injury, immediately after injury, 7 h post injury and 24 h post injury. Representative images of the polarization state of (A) uninjured and (B) injured spinal cords shows a drastic change in the polarization state following spinal cord ablation. (C) The spinal cord is significantly depolarized at 7 h post injury compared to uninjured animals and is largely repolarized by 24 h post injury. ***P<0.05; n=5. Scale bar=75 μm.