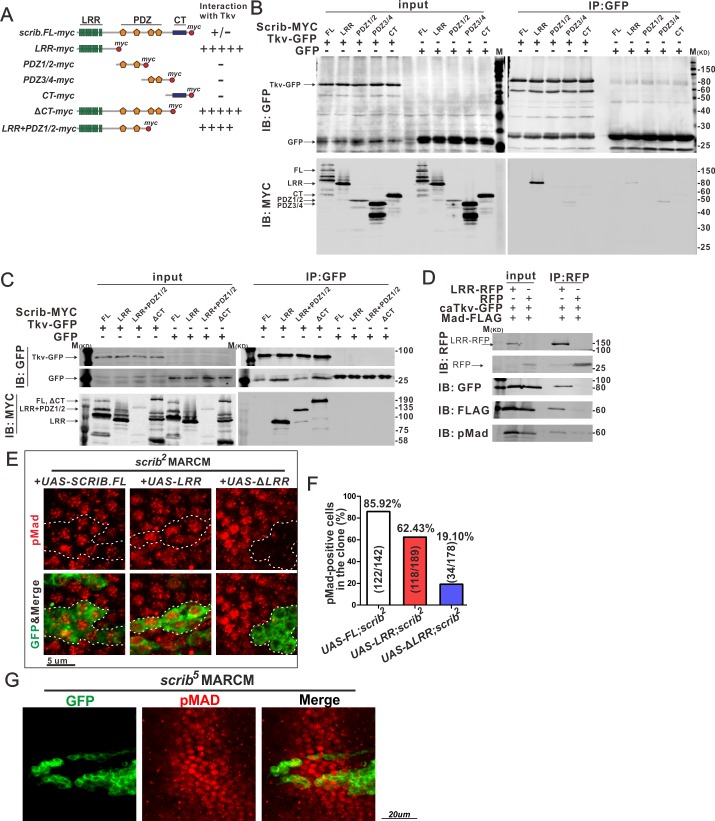
Fig 5. LRR domain of Scrib interacts with Tkv.
(A) Diagram of different fragments of Scrib. Intensities of interaction between Scrib fragments and Tkv are shown at the right. (B, C) Co-IP of Scrib (full length or fragments) and Tkv. Scrib-MYC and Tkv-GFP were expressed in S2 cells, and cell lysates were immunopreciated by anti-GFP. Cell lysates (input) and immunoprecipitated proteins (IP: GFP) were analysed by Western blots probed with anti-GFP and anti-MYC antibodies. (D) Co-IP of LRR, Tkv and Mad. LRR-RFP, caTkv-GFP and Mad-FLAG were expressed in S2 cells, and cell lysates were immunopreciated by anti-RFP. Cell lysates (input) and immunoprecipitated proteins (IP: RFP) were analysed by Western blots probed with anti-GFP, anti-FLAG and anti-pMad antibodies. (E) Expression of Scrib (full length), LRR domain or Scrib without LRR domain in scrib mutant clones labeled by GFP. pMad staining in PCV region at 24 h AP. Dashed lines delineate the clone boundaries. (F) Quantification of pMad-positive cells in E. (G) Effects of scrib5 mutant clones on pMad (red) at 24 h AP in the PCV region. Mutant GFP-labeled cells (green) were generated using MARCM. Results shown are representative of one of three independent experiments (B-D).